The Definitive Guide to Legal Document Assistant Software
The Definitive Guide to Legal Document Assistant Software
As much as most legal professionals would hate to admit it, paperwork takes up a huge chunk of their time. And in an industry where time quite literally translates to money, every minute is valuable.
Luckily, legal software is catching up to speed. Today, legal document automation software is solving the ever-present problem of drafting, editing, and finalizing legal documents manually. Traditionally, this process takes up hours—if not days—of work, time that could otherwise be spent on more valuable tasks.
So, how does document assistant software help reduce this bottleneck?

What is Legal Document Assistant Software?
Legal document automation software is an advanced technology solution designed to automate and improve the creation, management, and storage of legal documents. In essence, this type of software is meant to replace traditional, tedious methods of document handling with a digital approach.
Picture it as a virtual assistant for lawyers and law firms, programmed with knowledge of legal processes and terminology, streamlining the documentation process tenfold.
More specifically, legal document automation software simplifies tasks such as compiling, formatting, and customizing legal documents based on specific client information and needs through automation and artificial intelligence (AI).
Why Should You Use Legal Document Automation Software?
As automation technology becomes more and more common in the legal industry, legal document automation software has become a necessity rather than a need. Law firms that want to gain a competitive edge and improve their overall legal workflows adopt this type of tech for:
Increased Efficiency
One of the most immediate benefits of legal document automation software is the dramatic improvement in operational efficiency. By automating routine tasks, such as drafting standard legal documents, your firm can allocate its resources and time more effectively.
Automation reduces the manual effort involved in creating and managing documents, allowing your team to handle a larger volume of work without increasing headcount or hours worked.
Plus, less time spent on tedious work means more time to work on higher-value, profit-producing tasks.
Healthier Work-Life Balance
Better work efficiency goes hand in hand with a more positive work-life balance.
Reducing the time needed to create documents saves lawyers and paralegals hours of time that they can spend outside the office instead of being buried under paperwork.
Greater work-life balance leads to a whole other slew of benefits in any workplace. For one, lawyers with less workload than necessary tend to be more productive, collaborative, and satisfied with their jobs.
Faster Turnaround Time for Legal Documents
Clients expect prompt service, and the ability to quickly turn around accurate and professionally prepared documents can set your firm apart from the competition.
Legal document automation software streamlines the document creation process, from drafting to approval and signing. In turn, a sped-up process allows you to make new documents and meet tight deadlines with ease, which improves client satisfaction and potentially increases client retention and referrals.
Improved Document Accuracy and Consistency
Accuracy in legal documents is non-negotiable. Errors, inconsistencies, or omissions can lead to serious legal and financial consequences for your clients and your firm.
Automation software minimizes the risk of human error by using pre-set templates and conditional logic to ensure that documents are correctly formatted and contain all the necessary information.
By standardizing the document creation process, the software ensures that every document reflects the firm’s highest standards of accuracy and professionalism, regardless of who in the law office creates it.
Increased Law Firm Profitability
All of these benefits culminate into the ultimate end goal: better law firm profitability.
First, by streamlining document-related processes, your firm can handle more cases without a proportional increase in costs, thereby improving your profit margins.
Second, the time saved on document management can be redirected towards billable hours or developing new business, further increasing revenue.
Additionally, the enhanced client satisfaction resulting from faster turnaround times and error-free documents can lead to repeat business and referrals, contributing to long-term profitability.

What Legal Documents Can You Create with Automation Software?
Legal document assembly software can automate the assembly of many different documents. However, you need to find a document automation platform that covers the specific types of documents you want to automate.
So far, the software available today covers the following document types:
- Requests for Production
- Requests for Admission
- Interrogatories
- Contract agreements
- Incorporation documents
- Wills, trusts, and powers of attorney
- Employee contracts and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs)
- Demand letters
- Eviction notices
Features to Look For in the Best Document Automation Software
While document automation software sounds like a dream for legal professionals, keep in mind that not all platforms are made equal. If you want to reap all the potential benefits of this type of tech, be on the lookout for key features:
Legal Document Templates
Look for a platform with a comprehensive library of customizable legal document templates that cover a wide range of your needs, ensuring you can quickly start drafting without building from scratch.
If you use a specific set of templates, good legal software will let you upload them and learn from your templates to generate future documents.
Library and Storage
Most document automation platforms have built-in document storage, but you will want those documents to be accessible from anywhere.
Opt for cloud-based platforms that allow easy access to documents from any device at any time and have robust search functionalities for efficient document retrieval.
Extended File Types
Legal professionals will have to produce documents in various formats other than Word Docs, so it’s crucial to choose a document automation software that supports all common file types, such as Microsoft Word and PDF.

Conditional Logic and Auto-Population
The mantra of conditional logic is simple: “If this, then that.” This powerful feature allows for the development of custom workflows tailored to the specific needs of the documents you’re generating.
For instance, if you’re creating discovery phase documents, the software can automatically cue up a discovery request or response template for use.
Closely tied to conditional logic, auto-population is a feature that further enhances the efficiency of document assembly.
Using the litigation scenario as an example, once the software selects the appropriate discovery request template based on the conditional logic, it doesn’t stop there. It also fills in the client’s information across the necessary fields within the document.
This capability extends beyond just the data inputted for the current document; it can pull and populate information from across your document assembly or practice management software.
The result? A significant reduction in redundant data entry and a boost in the accuracy of the information within your documents.
Collaborative Features
Collaborative tools allow multiple team members to work on the same document at the same time, so they can track changes, provide feedback, and make real-time updates.
This feature enhances the efficiency of document generation and also ensures that all contributions are harmonized, maintaining document integrity.
These collaborative features are particularly beneficial in remote work settings. They ensure that geographical distance does not hinder teamwork and productivity.
Electronic Signatures
Getting clients and other legal professionals to sign documents in person just isn’t practical all the time. And frankly, it can be a huge waste of resources getting those documents back and forth.
Luckily, electronic signatures eliminate the need for physical documents, reducing turnaround times and enhancing the security of sensitive information.
This feature facilitates a smoother transaction process, enabling legal agreements to be executed promptly and efficiently, thus accelerating the completion of legal procedures.
Software Integration
Choose a document automation tool with the ability to integrate seamlessly with other software systems that your firm already uses. This includes case management systems, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platforms, email services, and more.
Such integrations create a unified workflow, allowing for smooth data transfer across different applications and reducing manual data entry. By connecting various aspects of a law firm’s operations, software integration ensures that information is consistently up-to-date and accessible, streamlining processes and enhancing overall efficiency.
Plus, you can get the tool up and running in no time and with almost no learning curve.
How Much Does Legal Document Assembly Software Cost?
The pricing models for legal document automation software vary widely, depending on the features, capabilities, and scalability of the platform.
Some platforms may offer a subscription-based billing model, where law firms pay a monthly or annual fee based on the number of users or the scope of features required. Others may offer a one-time purchase price coupled with ongoing support or update fees.
Plus, it’s important to consider the broader cost implications, including the potential cost of switching to new software, the time and effort involved in setup, how the system fits with existing legal workflows, and security considerations.
The right legal practice management software should simplify automating and managing documents, ideally integrating seamlessly with your firm’s existing tools and workflows to avoid time lost in switching between applications.
How Briefpoint Can Upgrade Your Legal Document Workflow
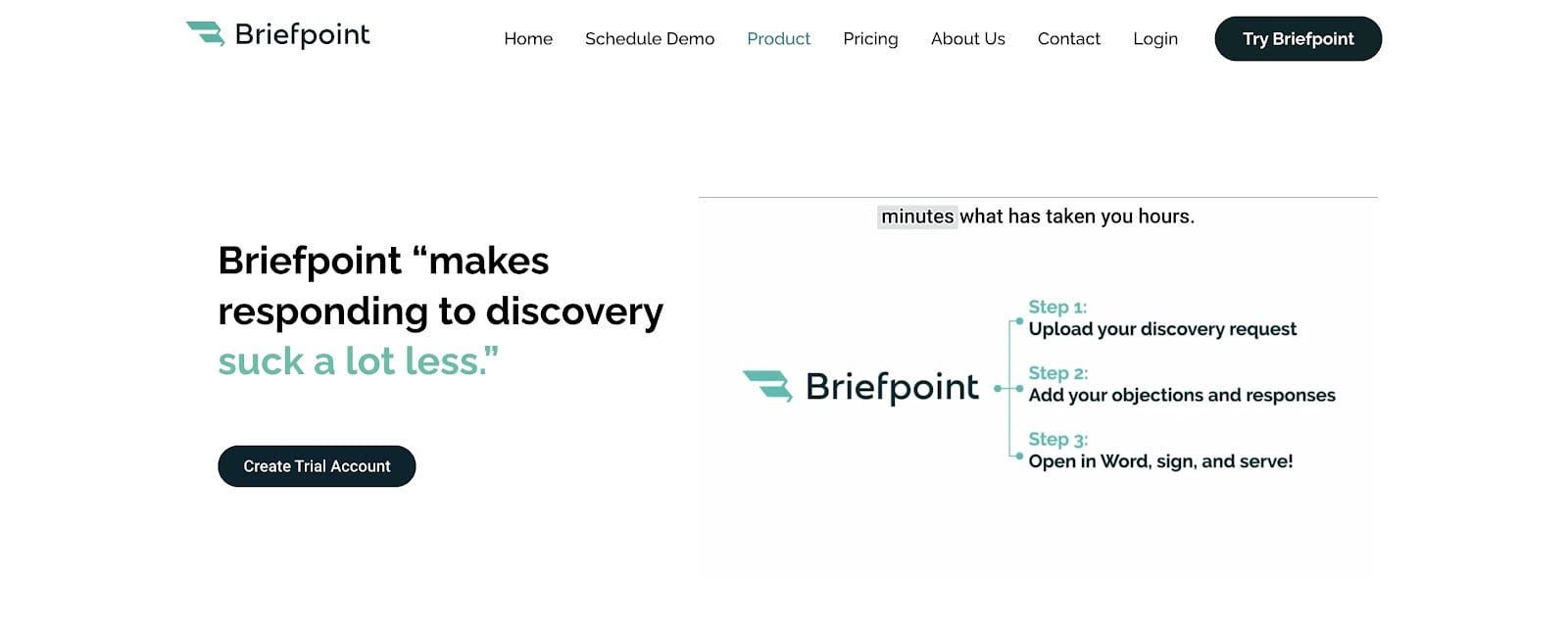
There are a lot of document assistant tools out there, but if you want to focus on discovery document automation, Briefpoint is the software you need.
Briefpoint works by automating the preparation of discovery request and discovery response documents, including but not limited to:
- Requests for Production
- Requests for Admission
- Interrogatories
The process is simple. Briefpoint automates the creation of discovery documents through a few key steps:
- Upload Discovery Request: Begin by uploading the discovery request document into Briefpoint.
- AI Analysis: The software uses AI to analyze the document and extract relevant information.
- Add Objections and Responses: You can then easily add any objections and responses within the platform.
- Download and Finalize: Once you’ve added your input, download the document and make any final adjustments in Microsoft Word.
Don’t let the discovery phase drag on longer than it has to. Use Briefpoint to generate documents in minutes instead of hours and use the extra time for more important tasks.
Generate Legal Documents in Minutes
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
FAQs About Legal Document Automation Software
Is legal document automation software difficult to implement?
While any new technology comes with a steep learning curve, most legal document automation software is designed with user-friendliness in mind. Many providers offer training and support to ensure smooth implementation.
Can I customize documents to fit my firm’s branding?
Yes. Most software allows for customization of word templates, not just in content but also in the overall look and feel of the documents, ensuring they align with your firm’s branding.
Is my data safe with legal practice management software?
Security is a top priority for reputable software providers. Look for software that offers encryption and complies with industry-standard data protection regulations.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
7 Best Productivity Tools for Lawyers In 2024
7 Best Productivity Tools for Lawyers In 2024
Lawyers, while often trapped under time-consuming tasks, are now taking advantage of legal AI tools to maximize their productivity and, in turn, their bottom line.
Whether you’re looking for a tool to draft your legal documents or document management software that can keep your data secure, there’s an app for you. In this article, we’ll go over the best productivity tools for lawyers to help you narrow down your search.

What Can Productivity Tools Do For Law Firms?
From the name itself, productivity apps aim to improve productivity in your law firm. However, this is too broad of an observation to take at face value.
Let’s examine how these tech tools are helping revolutionize the legal industry.
Streamlining Workflows and Improving Efficiency
The main goal of legal productivity apps is to simplify workflows and make them more efficient. In turn, lawyers and legal assistants spend less time on repetitive tasks and can instead devote more hours to high-value work.
When you look at the bigger picture, better efficiency cascades into more advantages, such as a healthier work culture, better career development, improved client satisfaction, and a more positive bottom line.
Promoting Better Time Management
Time management is crucial in the legal profession, where billable hours determine profitability. Productivity tools come equipped with time-tracking features and task management systems that help lawyers prioritize their workload and keep track of deadlines.
These tools help lawyers allocate their time more effectively by providing a clear overview of where time is spent, ensuring that every minute counts. Consequently, they have a better idea of how to maximize their billable tasks.
Plus, better time management helps lawyers achieve a better work-life balance and, ultimately, a more positive outlook towards work.
Upgrading Accuracy and Consistency
In the legal industry, accuracy is non-negotiable. A single mistake can have significant ramifications and hurt your bottom line–not to mention the impact on your law firm’s reputation.
Productivity tools improve accuracy and consistency across all documents and communications. From automated spell-checkers to document templates that follow firm-specific guidelines, these tools ensure that every piece of work meets the highest standards of precision.
Improving Client Satisfaction
In today’s digital age, clients expect quick responses and transparent communication. Productivity tools make this possible by offering platforms for secure messaging, document sharing, and real-time updates on case progress.
Aside from keeping clients on the same page, these tools also foster a sense of trust and reliability, improving overall satisfaction and potentially leading to more referrals.
Maximizing Law Firm Profitability
Ultimately, the adoption of productivity tools can have a direct impact on a law firm’s profitability. By automating administrative tasks, lawyers can dedicate more time to billable work and client acquisition.
On the other hand, improved accuracy and client satisfaction can lead to repeat business and referrals, further increasing revenue. Additionally, streamlining operations and reducing the need for manual labor can help lower operational costs, which is another crucial factor in maximizing profitability.

7 Best Productivity Apps for Law Firms
The legal market is brimming with tools promising to revolutionize law firm operations. Yet only a handful truly deliver on their promises and benefits.
Here’s a curated list of tools that stand out, ensuring your firm can do more with less.
1. Best Document Automation Tool: Briefpoint.ai
Briefpoint is an AI-powered app that speeds up the discovery phase of litigation by generating discovery responses and request documents for you. Unlike manual document preparation, you can generate discovery documents in minutes instead of hours, saving you both time and money in the process.
The legal documents Briefpoint AI can auto-generate include but are not limited to:
- Requests for Production
- Requests for Admission
- Interrogatories
Aside from drafting your documents, Briefpoint will allow you to add objections or responses that are pre-drafted or customized by you. Then, you can download the document and finish it on Microsoft Word. Alternatively, you can upload your draft on Google Docs to work with other collaborators.
2. Best Legal Practice Management Software: Clio
Clio stands out as a comprehensive legal practice management platform, offering features that cover nearly every aspect of running a law firm.
From case management to time tracking, billing, and client communication, this project management software provides a centralized system that helps law firms manage their operations more efficiently. Plus, its easy-to-use interface makes the learning curve as minimal as possible, which is a must for busy lawyers.
Its cloud-based nature also allows for easy access to information from anywhere, making it an excellent tool for firms with remote or hybrid work arrangements.
3. Best Note-Taking App: Evernote
Evernote is a versatile note-taking app that allows legal professionals to capture, organize, and share notes in various formats, including text, images, and voice memos. Its powerful search capabilities make it easy to retrieve information when needed, and its syncing feature ensures that notes are accessible across all devices.
Overall, Evernote’s ability to create, categorize, and manage notes makes it a valuable tool for keeping track of case details, research, and to-do lists.
4. Best Cloud Storage Solution: OneDrive
OneDrive offers excellent cloud storage solutions that are particularly beneficial for law firms, providing secure and scalable storage options for documents and files. Plus, it’s a safe document management software that will keep sensitive law firm data secure through its multiple high-tech encryption and two-factor authentication abilities.
With features like file sharing, collaboration, and remote access, OneDrive clears the way for seamless teamwork among legal professionals and attorneys practicing law outside the office, allowing them to work on documents simultaneously and access files from anywhere.
Its integration with Microsoft Office Suite further upgrades productivity within a law firm. It lets you store and access various Microsoft file formats, such as Word, PowerPoint, and Excel.
An honorable mention is Google Drive, which is the best option for law firms that use Google Suite instead of Microsoft Office. Both platforms are well-functioning and intuitive.
5. Best Law Library: Fastcase
A good law library is an indispensable app for any law firm. Fastcase provides comprehensive access to a vast database of legal resources, including case law, statutes, regulations, court rules, and constitutions.
Its advanced search tools and intuitive interface enable lawyers to conduct efficient legal research, find relevant precedents, and stay updated on legal developments. This legal technology can help any law firm save hours–if not days–of time spent on due diligence.
6. Best Legal Billing Software: Bilr
Last but not least, we have Blir. This software is designed to streamline the billing process in law firms, offering features like time tracking, invoice generation, and payment processing.
It helps reduce the administrative burden associated with billing, ensuring that firms can accurately and efficiently manage client accounts and finances. Bilr’s focus on legal billing makes it a tailored solution that addresses the specific needs of law firms, contributing to smoother financial operations.
7. Best Secure Communication App: Slack
Slack is a popular messaging app designed for team communication and collaboration. It provides a centralized platform for messaging, file sharing, and integration with other productivity tools, making it easier for teams to stay connected and work together efficiently.
Slack also has a built-in calling feature, so you can make phone calls from your desktop or mobile device, but take note that you can only make voice calls with one person on the free version.
Plus, you can create multiple channels with each dedicated to a separate legal department or team. The app also lets you share and access documents directly in the conversation for effortless collaboration. Better yet, this app integrates with other tools commonly used by law firms, such as Clio, OneDrive, and Evernote.

Stay Up to Date with the Best Productivity Tools
The rising demand for faster, better legal services pushes law firms to adapt to modern solutions that can maximize their efficiency tenfold. If your law firm struggles to maintain productivity, it might be time to integrate these tools into your current workflows.
However, how do you know where to start? A good rule of thumb is to begin with the most time-consuming tasks you have. For many law firms, this includes discovery document preparation.
Make the discovery phase faster, more accurate, and more efficient with Briefpoint AI. While Briefpoint auto-generates your legal documents, you can focus on tasks that require more brain power–which are also often the tasks that help you win the case.
Maximize Your Productivity With Document Automation
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
FAQs About Legal Productivity Tools
Can these tools integrate with each other?
Absolutely! Many of these tools offer integration capabilities, allowing for a seamless workflow between different applications.
Are these tools suitable for small law firms?
Yes, these tools are designed to cater to law firms of all sizes, offering scalable solutions that grow with your practice.
What about data security?
Data security is a top priority for these tools, with robust encryption and compliance measures in place to protect your firm’s and clients’ information.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
5 Legal Workflow Examples You Can Implement for Maximum Efficiency
5 Legal Workflow Examples You Can Implement for Maximum Efficiency
The rise in demand for legal work post-pandemic, the emergence of workflow automation tools, and the ever-present competitive environment in the legal industry–these factors call for better-than-ever efficiency levels in 2024 if you want your law firm to stay ahead.
In this article, we’ll go over the basics of legal workflow automation, how it can benefit your law firm, and the 5 best examples of workflow automation you can implement today.

What is a Legal Workflow?
A legal workflow consists of a series of tasks and processes designed to accomplish a particular legal objective or outcome. It serves as the foundational blueprint that directs your team in managing cases, from the initial client intake to the final billing process.
What is Legal Workflow Automation?
Legal workflow automation is the application of technology to simplify and automate typically tedious tasks within legal processes. Legal automation technology allows law firms and legal departments to design, execute, and manage legal workflows with minimal manual intervention.
More specifically, incorporating software tools and applications lets legal professionals automate various tasks such as:
- Document drafting automation
- Client intake processes
- Case management
- Billing and invoicing
- Contract review
- Compliance checks

What Are The Benefits of Legal Workflow Automation?
Automating legal workflows can make life easier for everyone on your legal team in many ways. In turn, a more productive legal department contributes to a better bottom line. Here’s a closer look at how legal workflow automation benefits the legal industry:
Streamlining Operations
Automating the grunt work – the repetitive tasks that bog down daily operations – not only speeds things up but also lets your team focus on more valuable, more complex aspects of legal work.
Reduced Risk of Errors
Automation reduces the likelihood of human error in document creation, data entry, and other processes.
Improved Client Satisfaction
Automation can lead to faster response times and more consistent communication with clients. It means you’re always a step ahead, from seamless onboarding to timely updates, leading to higher satisfaction and retention rates.
Enhanced Collaboration
Legal workflow automation tools often come with features that improve communication and collaboration among team members. Shared access to documents, automated task assignments, and progress tracking help keep everyone aligned and informed.
Cost Savings
Automating legal workflows can result in significant cost savings over time. It takes the manual labor out of many non-billable tasks, allowing you to redirect your team’s efforts to areas that need human insight. In the long run, this strategic allocation of resources pays off.
Scalability
When your workload increases, automated systems can handle the extra demand without needing to proportionally increase your staff. This makes scaling up smoother and more manageable, letting you expand your business without the growing pains.
Data Security and Compliance
Many legal workflow automation tools incorporate advanced security features to protect sensitive information. Plus, by automating processes, you’re also ensuring that your operations are in line with regulations and internal policies, thanks to standardization and detailed activity logs.
Strategic Insight and Decision Making
Automation tools often include analytics and reporting capabilities, providing law firms with valuable insights into their operations. This information is particularly useful when it comes to making strategic decisions, spotting areas for further improvement, and identifying new opportunities for automation.
5 Legal Workflow Examples You Can Replicate
You can apply automation to various administrative tasks to improve your overall efficiency and productivity. Below are five actionable legal workflow examples that you can easily emulate to harness the power of automation in your legal practice:
1. Client Intake/Onboarding
Legal teams can apply automation to the client intake and onboarding process to ensure a smooth and professional first impression. You can:
- Use online forms and document management systems to collect client information
- Automatically run conflict checks
- Generate onboarding paperwork
Here’s an example of an automated client intake process:
Step 1: Initial Contact
Clients start by filling out a detailed contact form on your law firm’s website. This form collects preliminary information, such as the client’s name, contact details, and a brief description of their legal issue.
Upon submission, the client immediately receives an automated email acknowledging receipt of their inquiry and outlining the next steps.
Step 2: Conflict Check
The information from the contact form is automatically fed into your firm’s conflict check system. If no conflicts are identified, the process moves to the next step. If a conflict is found, an automated response informs the client that the firm cannot represent them due to a conflict of interest.
Step 3: Intake Questionnaire
Clients who pass the conflict check receive an email with a link to a more comprehensive intake questionnaire. This questionnaire is designed to gather detailed information relevant to their case.
The questionnaire includes the ability to securely upload relevant documents.
Step 4: Consultation Scheduling
After submitting the questionnaire, clients are directed to an online scheduling tool integrated with the firm’s calendar. They can choose a convenient time for a consultation, either in-person or virtual.
Once a consultation is scheduled, both the client and the attorney receive an automated confirmation email with the appointment details and a calendar invite.
Step 5: Onboarding Documents and Agreement
Based on the information provided in the intake questionnaire, the system automatically generates onboarding documents and a customized agreement.
Clients can review and e-sign the agreement and pay the initial retainer fee online through a secure payment gateway.
Step 6: Welcome Package
Upon completion of the onboarding process, clients receive a welcome email. This email includes an introduction to their legal team, what they can expect moving forward, and how to communicate with the firm.
The email also provides login details for a client portal where they can track the progress of their case, communicate with their attorney, and access documents.
Step 7: Internal Notification
Once a new client is successfully onboarded, relevant legal teams are automatically notified through the firm’s internal communication system. This ensures that everyone involved is up-to-date and ready to start working on the case.
2. Client Communications
Automating client communications is an excellent approach to upgrading client engagement and satisfaction, ensuring consistent and timely interactions throughout the legal process. Here’s an illustrative process for automating client communications within your law firm:
Step 1: Automated Onboarding Messages
After a client is successfully onboarded, they receive an automated welcome message. This message outlines what they can expect in terms of communication and introduces them to their legal team.
Step 2: Case Updates
Set up a system to send automated updates on case progress at predetermined intervals or after specific milestones are achieved.
Step 3: Appointment and Deadline Reminders
Implement an automated reminder system that notifies clients of upcoming appointments, important dates, and deadlines via email or SMS.
Step 4: Automated Check-ins
For long-duration cases or for clients with whom you wish to maintain a relationship, set up automated emails or messages that check in on them periodically. These communications can offer assistance, provide relevant legal updates, or share useful content.
Step 5: FAQ and Resource Sharing
Automate the distribution of FAQs, guides, and resources relevant to the client’s case or legal needs. This proactive approach can address common questions and concerns, reducing the need for direct inquiries.
Step 6: Billing and Payment Reminders
Automate billing reminders and payment confirmations to streamline the financial interactions with clients. This way, you can ensure transparency and reduce the administrative burden of managing payments.
3. Legal Document Automation
Legal document automation revolves around generative artificial intelligence (AI). This subtype of legal AI is designed to automatically draft various legal documents, such as contracts and discovery documents, to cut down manual processes involved in document generation.
These are the documents that legal professionals usually automate:
Discovery Response and Request Documents
Busy law firms can use generative AI to draft discovery response and request documents (e.g., requests for production, requests for admission, interrogatories) that would otherwise take hours to make.
Contracts and Agreements
Legal workflow software quickly generates standard contracts, service agreements, lease agreements, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), employment contracts, and partnership agreements with customized details for each party involved.
Legal Letters and Correspondence
Templates for letters of advice, demand letters, cease and desist letters, and other formal legal communications allow for quick customization for various scenarios.
Court Forms and Pleadings
Certain types of software can automate the inclusion of relevant case and party information in standard forms and pleadings for court filings, including complaints, motions, affidavits, and judgments.
Estate Planning Documents
Legal teams can customize wills, trusts, powers of attorney, and healthcare directives to fit the specific needs and circumstances of the client.
Real Estate Documents
Some legal practice management software can efficiently produce purchase agreements, deeds, closing documents, and landlord-tenant agreements, such as leases and eviction notices.
4. Law Firm Billing
Implementing automation in law firm billing practices can transform the management of financial transactions, improving the efficiency, accuracy, and transparency of billing operations.
Here’s a breakdown of how law firms can automate their billing process:
Step 1: Time Tracking Integration
Implement software that legal teams can use to track their time spent on different cases automatically. This helps ensure accurate billing and minimizes the chance of unbilled work.
Step 2: Generating Invoices
Based on the time tracked and the specific billing arrangements with clients, the system automatically generates detailed invoices for billable hours. These invoices can include descriptions of the services rendered, the time spent, and the applicable rates.
Step 3: Customization and Review
Allow for customization of invoice templates to meet the firm’s branding and client’s preferences. Before sending, your legal team can review and adjust invoices if necessary, ensuring accuracy and client satisfaction.
Step 4: Electronic Delivery
Use the billing system to email invoices directly to clients, reducing paper waste and speeding up the delivery process. Electronic delivery also makes it easier for clients to review and pay their invoices.
Step 5: Online Payment Options
Integrate online payment solutions that allow clients to pay their invoices via credit card, ACH transfer, or other online payment systems. This convenience can significantly shorten the payment cycle and improve cash flow.
Step 6: Payment Tracking and Reminders
The billing system should automatically track payments received and reconcile them with the corresponding invoices. For overdue invoices, the system can send out automated payment reminders to clients, encouraging timely payments.
Step 7: Financial Reporting
Utilize the billing software to automatically generate financial reports, providing insights into the firm’s financial health, productivity, and outstanding receivables. These reports are essential for effective financial management and planning.

5. Task Management
Workflow automation plays a big role in task management, involving the use of various types of software to streamline the planning, delegation, tracking, and completion of tasks and projects.
This technology helps law firms improve time management and accountability and ensure that critical deadlines are met without overwhelming manual oversight.
Here are several examples of automated processes for task management:
Case Intake and Assignment
A new case is entered into the firm’s case management system through an online form submission by a potential client.
The system automatically performs a conflict check and, if cleared, assigns the case to an attorney based on expertise and current workload. The assigned attorney receives an email notification about the new case.
Initial Review and Client Communication
The assigned attorney marks the case as “reviewed” in the system.
The system automatically generates an introductory email to the client, providing the attorney’s contact information and scheduling a kick-off meeting using a link to the attorney’s calendar.
Document Request and Collection
After the kick-off meeting, the attorney identifies the documents needed from the client.
The system sends an automated email to the client with a secure link to upload the required documents. A follow-up reminder is scheduled if the client does not respond within a specified timeframe.
Task Delegation and Monitoring
Documents are received from the client.
The system creates tasks for document review and analysis, assigning them to appropriate team members. Each team member receives a notification of their assigned tasks with deadlines. The system tracks progress and sends reminders as deadlines approach.
Billing and Time Tracking
Tasks related to the case are marked as completed.
The system logs billable hours associated with completed tasks and generates a draft invoice for the attorney’s review. Once approved, the system sends the invoice to the client with payment instructions.
Legal Workflow Automation Software Overview
These examples of legal workflow automation make the benefits of automation clear. Each automated workflow eases the burden on legal teams, creating more room for more important legal matters and other strategic tasks. The cumulative result? More satisfied clients and increased law firm profitability.
Don’t know what legal workflow automation software to start with? Consider automating the most tedious part of litigation first, the discovery phase.
Briefpoint AI is a law firm automation tool that offers invaluable litigation support by automating discovery requests and response documents. With Briefpoint, you can save valuable time on these routine tasks and ensure consistency in all your documents, including but not limited to:
- Requests for Production
- Requests for Admission
- Interrogatories
Take Advantage of Legal Automation with Briefpoint
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
FAQs About Legal Workflow Automation
Won’t automation make our jobs obsolete?
Quite the opposite! Automation takes care of the mundane tasks, allowing legal professionals to focus on higher-level, strategic work.
Is legal workflow automation expensive?
It’s an investment. While there’s an upfront cost, the long-term savings in time and resources can be substantial.
How technical do we need to be to implement automation?
Not very. Many legal workflow automation tools are designed with user-friendliness in mind. Plus, most providers offer training and support.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information. This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser.
Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
Top 6 Legal Industry Trends to Keep an Eye On in 2024
Top 6 Legal Industry Trends to Keep an Eye On in 2024
Law is known as one of the industries most resistant to change, with many law firms sticking to traditional methods–but not without a good reason. These traditions have built some of the biggest practices that we know today, and they undeniably influence other firms to stick to what they know best.
All that is changing, however, with the arrival of new legal tech and constant innovation of standard legal practices. In 2024, we expect to see both big and even smaller law firms ride the wave of transformation in the field of law, and just like you, we can’t wait to see what the new year has in store for us.
Let’s take a look at some of the biggest legal trends in the industry today.

6 Latest Legal Trends to Watch Out For
The legal sector is highly competitive and fast-paced by nature, which calls for constant improvement through strategies that align with current innovations available. There are too many legal trends to talk about, so we’ve narrowed it down to the six most relevant ones:
1. Increased Adoption of Artificial Intelligence Technology
Lawyers are turning to artificial intelligence to simplify legal processes and make them more efficient, made noticeable with the popularization of legal AI tools like Briefpoint, PatentPal, and Casetext. Most legal pros are no longer skeptical of this “new” tech but are instead embracing it as a nifty and cost-efficient legal assistant.
A LexisNexis survey involving nearly 8,000 participants across US, Canada, France, and UK law firms revealed that almost half expect AI to significantly change practices, especially in improving productivity and efficiency in everyday tasks.
Meanwhile, Thomson Reuters highlighted 2023’s milestones in AI development, including a focus on safe and trustworthy AI applications in various legal functions.
2. The Rise of Cloud-Based Technology for Cybersecurity
Private cloud tech is a type of cloud-based computing and storage where the data belongs to the law firm that uses it, inaccessible to the public. The legal field handles sensitive and private client information daily, making private clouds a necessity as more and more firms go fully digital.
But why has cloud tech become so crucial?
The 2022 IBM Cost of Data Breach report showed that a staggering 83% of the organizations it surveyed had encountered more than one data breach, facing an unprecedented average total cost of $4.35 million—a peak for the year and marking a 2.6% increase from the year before.
Cloud security encompasses a wide array of protocols, tools, and strategies aimed at safeguarding data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud, addressing key concerns such as data privacy, compliance, and protection against breaches and malware.
3. More Acceptance of Alternative Legal Service Providers and Fees
Simply put, Alternative Legal Service Providers (ALSPs) are services that take the grunt work from in-house legal teams. These might include document review, due diligence, research, compliance, and much more.
According to several reports, ALSPs now constitute a $20.6 billion market segment, having experienced a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% from 2019 to 2021. This growth indicates a rapidly evolving market where the lines between ALSPs merged firms, law firms, and corporate law departments are increasingly blurring.
The report highlights that both law firms and in-house counsel are recognizing the value that ALSPs bring to the table, including specialized services, improved cost efficiency, and greater flexibility in headcount and talent management.
Independent ALSPs represent the largest market segment, but law firm-owned captive ALSPs are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, indicating a strategic shift within law firms towards embracing alternative service models.
4. Shortening Lockup Periods with Technology
Most firms rely on billable hours to make a profit, but these hours don’t necessarily get paid right away. A “lockup period” refers to the time between completing work and getting paid. For larger firms, longer lockups may not make a significant change to cash flow, but it can be a huge problem for small firms with limited resources.
The 2023 Legal Trends Report by Clio emphasized the importance of reducing lockups for maintaining a healthy cash flow. It introduced the concept of “lockup” as a mix of “realization lockup” (work yet to be billed) and “collection lockup” (billed work yet to be collected), suggesting that technology, particularly electronic billing solutions, can significantly lower these durations.
Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer, for example, has been focusing on reducing lockup by implementing internal strategies to decrease the waiting time for client payments. This effort is a response to the increase in lockup days, indicating a broader industry trend toward prioritizing faster billing and collection processes to improve financial health.
5. Rising Numbers of Freelance Lawyers
Some people might think that the legal profession is something you have to do on-site, inside an office where you can meet colleagues and clients face-to-face. That’s not the reality nowadays, especially with current technological advancements and shifting work preferences brought about by the pandemic.
Today, the legal world is adopting alternative work setups, as we can see by the increasing number of freelance lawyers. These attorneys come from diverse backgrounds, including law professors, lawyers caring for families, and retired or semi-retired legal professionals. There’s even a buzz about UK firms expanding their services to the US through remote work.
Overall, the appeal of remote work lies in the flexibility, work-life balance, and variety of projects, which contrasts with the traditional set-up.
Additionally, the increasing number of firms outsourcing work supports the rising trend of freelance lawyering. Nearly half of law firms reported using contract lawyers, indicating a significant shift towards integrating freelancers into traditional legal practice.
This change is partly driven by the legal outsourcing market’s rapid growth, which is projected to reach significant figures by 2027.
6. More Law Firms Focusing on Combating Recession
Many industries are still reeling from the economic impacts of the pandemic, and the legal sector is no different. Today, legal professionals are more wary of economic uncertainty and finding ways to be more recession-proof.
The resilience and growth strategies that were emerging in 2023 have further evolved this year, with firms focusing even more on diversifying their various business practice areas and enhancing operational efficiencies to maintain competitiveness and profitability.
Midsize law firms, in particular, have continued to thrive by capitalizing on counter-cyclical practices such as litigation, labor & employment, and bankruptcy. This focus allows these firms to leverage the demand brought about by economic shifts, providing services that become more sought-after in challenging times, such as the cost of living crisis.
Additionally, law firms are increasingly adopting strategic measures to maximize efficiency and profitability. These measures include optimizing leverage, further reducing office space in response to hybrid work models, investing in technology and skilled staff like pricing specialists, and outsourcing non-core functions.

The Future of the Legal Industry is Brighter Than Ever
The legal industry, while inherently orthodox in some ways, is not immune to change. Goals may remain the same, but the ways we go about it are always open for improvement.
As you can see, these key trends revolve around upgrading legal services and, essentially, the bottom line. With more efficient workflows and maximized potential, firms can stay competitive in a cutthroat legal market.
One way to embrace efficiency in your firm is to implement high-tech tools that minimize your tedious tasks, starting with the most time-consuming legal process of all: discovery. Briefpoint is a generative artificial intelligence tool that drafts discovery response and request documents for you, which would take the average lawyer hours–if not days.
With Briefpoint’s generative AI, you can focus on more value-adding work, produce consistent documents, and, ultimately, make your legal services a notch above the others.
Stay Ahead of the Competition with Briefpoint AI
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
FAQs About Legal Industry Trends
How can law firms integrate AI into their practices?
Start by identifying repetitive, time-consuming tasks that can be automated, such as document review or legal research. Investing in generative AI tools designed for these tasks can free up your team’s time for more complex work.
Are cloud-based cybersecurity solutions expensive?
While costs can vary, cloud-based solutions often offer scalable pricing models that can be more cost-effective than traditional IT infrastructure, especially when considering the potential cost of data breaches.
How can law firms make their billing more client-friendly?
Consider offering alternative fee arrangements, such as flat fees, subscription models, or success fees. Transparency and communication about costs are also key drivers of client satisfaction.
What should law firms do to prepare for a recession?
Diversify practice areas, focus on core competencies, reduce costs, and build a solid financial reserve. Strengthening relationships with existing clients and investing in marketing can also help maintain revenue streams and retain clients, which is especially beneficial for smaller firms.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
Best 5 Gavel Software Alternatives in 2024
Best 5 Gavel Software Alternatives in 2024
The best document automation software tools are easy to use and effective, and help law firms save significant amounts of time, which they can then spend on value-adding tasks.
In this post, we’ll review some of the best Gavel alternatives available to litigators and law firms.

Briefpoint
There are plenty of Gavel alternatives, but none can match Briefpoint for discovery document automation. Briefpoint makes it as easy as possible for law firms to automate the key discovery response and request processes, resulting in hours of saved time that lawyers can spend drafting what really matters.
Briefpoint has been built specifically with the legal industry in mind, making it intuitive for law firms to use. The powerful AI integrations ensure that it’s highly effective and makes working straightforward.
Thanks to Briefpoint’s intuitive design, while sophisticated, Briefpoint can nevertheless be used by professionals of all technical abilities.
The result? Hours saved on each document. You can get started with Briefpoint by scheduling a demo.
Rally
Rally is a law-focused automation tool that focuses on many legal tasks, not just document creation.
With Rally, you have control over many aspects of the client experience, and you can also use it to customize branding, organize documents, and accept payments.
While Rally is a powerful tool, it does have a couple of disadvantages. The main one is that it offers many different features that may not be required by the law firm, resulting in paying for a product that is not fully needed.
In addition, its document creation capabilities are not as advanced as other Gavel alternatives, such as Briefpoint. It also has a high price point.
However, it may be suitable for individual lawyers who want an all-encompassing tool with which they can complete a variety of tasks.
Hotdocs
HotDocs has been around for a long time, which is both a positive and a negative. On the plus side, they have experience in putting together forward-thinking document generation software.
However, because it’s been around for a while, it’s lacking some of the innovation that you’ll find in other tools. It also is not specifically designed for use in the legal field, which makes it a little more difficult for legal professionals to use.
It’s generally more complicated to use than other Gavel alternatives, with many of the tool’s features requiring coding experience. If you have coding experience along with the time to get to grips with HotDocs, then you’ll find it to be powerful. It’s also recommended if you serve a variety of different sectors, not just the legal field.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a software tool that’s easy to use and offers a wide variety of features, including legal document automation. It’s suitable for both large and small law firms and is adept at creating both complex and straightforward documents.
The software puts a greater emphasis on the client experience than other tools, and could well be regarded as a client onboarding tool rather than a document automation tool.
Still, it’s possible to create discovery responses and requests documents once you know how, and it also integrates with a number of tools widely used within the legal field.
PandaDoc
PandaDoc is a popular document automation software tool that claims to help professionals save up to 40% of time per document. It wasn’t specifically designed for use in the legal industry, but it includes a number of tools that legal professionals will appreciate.
It comes packed with features that help with various tasks beyond document creation, such as streamlining the customer experience. While powerful, it is more complex than other tools, and may not be suitable for firms looking to get up and running with their software quickly.
How Briefpoint Can Help You
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Under these assumptions, you save $20,477 using Briefpoint, per year, per attorney.
Test Briefpoint yourself by scheduling a demo here.
FAQs About Gavel Alternatives
What Can You Do With Legal Document Automation Software?
Legal document automation software helps to streamline the discovery response and request process. By spending less time on these time-consuming tasks, legal professionals can spend more time on value-adding tasks, all the while having confidence that their documents are just as they should be.
What Is The Best Gavel.io Alternative?
There are plenty of Gavel alternatives on the market. One of the best is Briefpoint, which offers automated discovery response and request documents. Featuring a high customer satisfaction score of 4.9/5, Briefpoint has become known for being one of the best AI legal tools in the industry, capable of reducing the time spent on each document by up to 87%.
What to Look For In Legal Document Automation Software?
Not all legal documentation automation software is the same, so it’s important to look through the Gavel alternatives and find the one that’s right for your needs. In general, it’s best to look at software that is effective, powerful, and easy to use — with those three attributes, law firms can ensure that they have a tool that can seriously enhance their productivity.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information. This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser.
Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
The Work Product Doctrine in California (2024 Guide for Litigation Attorneys)
The Work Product Doctrine in California (2024 Guide for Litigation Attorneys)
The Work Product Doctrine Overview
The work product doctrine is a fundamental aspect of California law that protects certain materials from disclosure or discovery in civil litigation. This article will delve into the principles and requirements of this doctrine, specifically covering the types of materials protected as work product, persons who may claim work product protection, exceptions to the work product doctrine, and waiver of work product protection.
Work Product Protection Purpose
The work product doctrine, codified in California law under Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 2018.010 et seq., serves two primary purposes: preserving the rights of attorneys to prepare cases for trial with necessary privacy and preventing attorneys from taking undue advantage of their adversary’s industry and efforts. Although the statute appears to apply only to discovery proceedings, courts have held that it also shields work product from disclosure at trial and extends to criminal proceedings.
What is Protected by the Work Product Doctrine?
In California, the work product doctrine provides two types of protection for attorney work product: absolute and qualified.
Absolute protection covers “a writing that reflects an attorney’s impressions, conclusions, opinions, or legal research or theories is not discoverable under any circumstances.” (Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 2018.030(a)) Qualified privilege covers the other work product of an attorney and “is not discoverable unless the court determines that denial of discovery will unfairly prejudice the party seeking discovery in preparing that party’s claim or defense or will result in an injustice.” (Cal. Code Civ. Proc. § 2018.030(b))
Who Owns the Protection?
Work product protection is a type of privilege that belongs to the attorney and may be claimed or waived by the attorney. However, it may also be claimed by the client on behalf of the attorney in the attorney’s absence. Additionally, a litigant acting in propria persona may assert the statutory work product protection on their own behalf.
Exceptions to Work Product Protection
Work product protection does not apply in certain circumstances, including actions between attorneys and clients involving breach of attorney’s duty, official investigations or proceedings involving alleged participation by attorneys in crime or fraud, and State Bar disciplinary proceedings.
Waiving the Protection
Work product protection may be waived through various means, such as disclosure or consent to disclosure, failure to assert the protection when the opportunity arises, placing certain matters at issue, or engaging in conduct inconsistent with claiming the privilege. Inadvertent disclosure of work product does not necessarily waive the protection, but receiving attorneys must act ethically and responsibly in such situations.
Conclusion
The work product doctrine is a vital component of California law that safeguards the attorney-client relationship and ensures that attorneys can effectively prepare for litigation. By understanding the principles and requirements of this doctrine, litigation attorneys can better navigate the complexities of the legal system and protect their clients’ interests.
Briefpoint Litigation Software
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Under these assumptions, you save $20,477 using Briefpoint, per year, per attorney.
Test Briefpoint yourself by scheduling a demo here.
Discovery Responses: How Can Software Help?
Discovery Responses: How Can Software Help?

Discovery Responses Overview
Responding to opposing an opposing party’s requests for information can be time-consuming and cognitively challenging. Unfortunately, many law firms have become accustomed to using manual paperwork to deal with these.
Now, though, software is helping. Law firms are experimenting with automation software like Briefpoint, to expedite the tedious work of drafting discovery responses and focus on what matters most.
The benefits of using software to automate discovery responses are substantial. Solutions reduce costs, minimize the risk of inadvertent disclosure of privileged information, and improve accuracy. Once law firms start using them, they often wonder why they didn’t discover them earlier.
This article explains how software solutions, like Briefpoint, can assist with discovery response. We cover the principal benefits and how AI-infused tools transform workflows.
Improving The Review Process
The primary benefit of discovery response software is its capacity to streamline the review process. Instead of reading through documents manually, systems crawl submissions for relevant information and extract it for evaluation.
For example, Briefpoint’s solution does this using advanced artificial intelligence (AI). It scans documents, pulls relevant information, and assists you in responding. Simply upload requests for admission/production or interrogatories and get a suite of tools for adding objections and responses.
Another benefit of software in the review process is helping avoid missing critical items in discovery requests, a common problem in legal practices. Attorneys and paralegals can sometimes skip crucial information when crafting responses. However, software solves this problem by using AI to extract anything essential. It never gets tired, reducing the risk of error or non-compliance.
Briefpoint makes this aspect of the review process simpler. AI then presents short reviewable snippets you can use when crafting your response. This helps with productivity and prevents tedious mistakes.
Building Strong Responses
While providing information to the opposing party is sometimes mandatory, it can put clients at an unnecessary disadvantage when done incorrectly. Therefore, software solutions also help you build strong discovery responses.
For example, software can integrate legal databases and relevant case law to support the integrity of your objections. It can also call on pre-filled template libraries (and fields), enabling you to “drop-and-drag” or simply click your responses into existence.
You choose from a list of legally permissible responses added automatically. It happens almost instantaneously. The best solutions let you draft documents with a click and apply standards across your firm.
For example, Briefpoint includes template responses and automatic objections you can add to your reply (that qualify under the law), saving an estimated 87% of your time. (You can download them into Word format to edit them further).
Software can also include automated filtering and tagging. These features scan documents, looking for keyphrases that indicate a request for privileged data. The most advanced tools use machine learning to look for confidential information. This technology streamlines the review process further and provides practitioners with greater confidence when submitting documents to the opposing party.
Enhanced Communication, Organization, And Security
Another benefit of discovery automation software is enhanced communication and collaboration. Team members can work in tandem to optimize replies and ensure optimal client protection within the law.
The best tools also enhance security, enabling you to comply with data protection laws within and across jurisdictions. For example, Briefpoint puts multiple measures in place to prevent data loss or theft. For instance, in-transit and at-rest encryption means that documents uploaded to us remain inaccessible regardless of location (except to those with permission).
We also perform regular document backups and maintain redundant servers to ensure you don’t lose any uploaded paperwork. On the backend, our team implements mandatory code reviews and conducts regular internal security audits on all technical decisions. And Microsoft Azure is our login security provider, compatible with multiple business-related accounts.
Understanding The Value Of Discovery Response Software
Ultimately, discovery response software tools help you cut the amount of non-billable time your team spends on discovery responses. Speeding up back-office processes enables you to operate more efficiently while assuring your clients’ best interests.
They also enable you to enjoy a host of additional benefits, such as avoiding disclosing privileged information and improving the accuracy of your responses. You can streamline your workflow and achieve peace of mind.
How Briefpoint Can Help You
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
FAQs In Relation To Discovery Responses
How do you respond to a discovery?
The best way to respond to discovery is to write each interrogatory and provide your response underneath it. Sometimes, you will provide the requested information, but other times you will want to list an objection. Briefpoint makes this process simple by providing a library of template responses you can use for variegated requests.
What happens if you don’t answer a discovery?
Failing to respond to a discovery can lead to various sanctions, including fines and penalties in the courtroom. It could also undermine your credibility.
What is a written discovery response?
A written discovery response is a document that provides a discovery request reply in writing. It can be electronic or mailed to the opposing party’s representative.
How do you write a discovery request?
Writing a discovery request requires extensive legal knowledge and understanding of permissible objections. However, software tools offer various shortcuts. For instance, BriefPoint can scan discovery requests and provide bespoke responses and objection suggestions based on the received text using AI.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information. This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser.
Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
Requests For Production: How To Automate Preparation In 2024
Requests For Production: How To Automate Preparation In 2024

What Is a Request for Production of Documents?
Requests for production are a legal procedure that is used during the discovery phase of a civil lawsuit or legal proceeding and is the asking of documents or other relevant items for the case to be presented.
These might be physical documents that need to be produced, or documents to simply be disclosed that could help the case move forward. It’s a vital part of the process that can enable both parties to gather evidence in preparation for trial.
It essentially asks the other party to produce any documents or other items that might be used as supporting evidence during a trial. If the other side claims that it doesn’t exist but then tries to produce it at the trial this can be objected to by the party to the judge. By requesting the documents ahead of time you can mitigate the risk of surprise evidence being produced during the court case.
Requests for production are a key part of the process and tend to include the following:
Specification of the exact documents required – The document should outline the documents, materials, or tangible assets that are required, being as clear and specific as possible. For example, listing the dates of bank statements.
The relevance of the items – The items that are requested must be directly related to the lawsuit issues and explicitly state why they are relevant. Vague or irrelevant requests could be objected to and the documents or assets not be disclosed.
The timeframe in which the items must be produced – You must add a reasonable timeframe for the documents/ other items to be handed over. This tends to be 30 days but can vary depending on the rules of the court, the jurisdiction, and other extenuating circumstances.
Why is a request for the production of documents so important?
A request for production is a vital part of the discovery process of a trial for many reasons. One of the first important things it does is allow parties to request and obtain relevant information that can support their defenses or claims.
These can help to build up evidence that can be used in a trial. It also enables transparency between both parties helping to prevent any surprises during the trial. This way both parties have the same information presented to them and can prevent a fair case.
The pre-presentation of documents before trial also enables attorneys to amend their case strategy accordingly, utilizing the information received to help add strength to their arguments and know what questions to put forth to the opposing party.
Another reason it’s so important is that it can help to streamline court proceedings, reducing time and helping to move the case along efficiently. It ensures the trial is fair and can aid in providing an efficient resolution for both parties in the case.
What are some key aspects of a request for the production of documents?
If a party feels the information requested is irrelevant, too vague, or wants privileged or confidential information they can object. This might need to be referred to the court to get further clarification and decide on the outcome of the matter.
There are specific rules regarding the format of the request for production. The court will set these rules which need to be followed. The request must be formally written and it must be very specific when outlining the exact information or items they are requesting.
What are some of the items that might be requested during a request for production?
Several items fall under a request for production and both parties must comply as much as they can. The items that might be called for include:
Documents
Physical documents can mean a number of different things, from letters and emails that have been sent to invoices, reports, bank statements, and invoices. It’s important to specify exactly what the documents are that are being requested and include as much detail as possible.
Photographs and Videos
Photos and video clips can be vital evidence during a court case. These could be taken at home, CCTV, or taken by a third party.
Physical objects
Physical objects might be requested in the case they could help provide vital evidence. These might be products or machinery that have relevance to the case.
Contracts and statements
You might request contracts such as phone or employment contracts, bank statements, agreements, or leases. They could help to prove (or disprove) certain aspects that have been put forward in the case by either party.
Medical Records
If the case has to do with someone having an injury or a claim relating to healthcare, medical records can be requested. This could include treatment plans, doctor reports, and any other related documents that could help. As this is confidential data it’s important to specify exactly what you’re looking for or your request might be denied or put forward to a judge.
Electronic Data
Electronic information is another thing that might be asked for. This can include any information such as text messages, emails, social media posts, website records, or computer files. Again, being specific is key for this. Try and include dates where possible to back up this.
Corporate Documents
If the lawsuit has to do with a work dispute, you could request corporate documents. This could include any policies, contracts, or documents related to the procedures of a company.
How To Automate Your Process
Utilizing automation software like ours at Briefpoint means you can focus your attention on the rest of the case. It automates the construction of commonly used litigation documents such as requests for production and is tailored to the document drafting processes you’ve already honed.
The platform can take an opposing counsel’s PDF discovery requests and transform them into professional discovery responses in next to no time. Once inside the dashboard, you simply upload the PDF, and the powerful tool will organize and list each request.
From there, you can select your objections and responses before asking the software to create a Word document, which can be edited and signed before being sent back to the opposing counsel or your CMS (case management system).
How Briefpoint Can Help
Discovery responses cost firms $23,240, per year, per attorney. $23,240 estimate assumes an associate attorney salary of $150,000 (including benefits – or $83 an hour), 20 cases per year/per associate, 4 discovery sets per case, 30 questions per set, 3.5 hours spent responding to each set, and 1800 hours of billable hours per year.
Book a demo and save on these costs with Briefpoint.
How to Develop a Relationship with AI Built on Trust
How to Develop a Relationship with AI Built on Trust

The release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT showcased the significant advancements in generative AI. As a result, various niche industries, including the famously archaic legal sector, have started to test the waters of high technology for the first time.
In this case, “generative AI” refers to a type of AI system known as a “transformer” that writes natural language one word at a time based on a combination of (a) statistical probability gathered from millions of samples of text and (b) human feedback. Due to the volume of text used to train these systems, transformers are also commonly called “Large Language Models” or “LLMs.”
However shiny, with all new tech comes new risks. Front of mind for litigation attorneys, none want to be made famous for citing fake cases in a brief.
Avoiding generative AI in light of this risk is not, however, the solution. As this article will outline, there are safe methods for employing generative AI in a manner that will not only increase efficiency – it will make you a better attorney.
By automating various tasks and surfacing key insights, generative AI has the potential to significantly enhance the work of any litigation attorney. According to Goldman Sachs, AI could automate up to 44% of legal tasks, giving attorneys who adopt this technology a competitive advantage. A LexisNexis survey revealed that 84% of legal industry respondents expect efficiency improvements due to generative AI.
When considering a generative AI solution, the critical factor is whether it can handle routine tasks that require memory but not creativity. Small law firms and solo practitioners, unable to develop their own AI platforms like Lexis AI, can still benefit from reliable alternatives in the market. Here is a list of areas where generative AI can be useful for litigation:
● Legal research
● Drafting discovery responses
● Locating and creating fact citations
● Generating fact statements and fact summaries
While exploring and adopting generative AI, addressing general concerns and reservations about its use is crucial. Ensuring the technology is employed effectively and safely will enable litigation attorneys to optimize their practices while maintaining professional standards.
General Guidelines for Using Generative AI
If you come across a generative AI company claiming their product has no downsides and can do all the work for you, approach it with caution. A good generative AI should be viewed as a supportive tool, not a replacement for a skilled litigation attorney. However, like any team member, it requires proper management.
When using generative AI, it is essential to understand how to utilize prompts effectively. A well-crafted prompt can significantly impact the quality of the output. For instance, in brief writing, the appropriate prompt can adjust the tone to suit the desired work product.
This process involves asking specific questions and using the correct language to obtain the desired results, similar to the search operators you are familiar with. The ideal prompts will vary depending on the generative AI, so ensure you read the relevant company’s instructions.
Once you have the generated content, rely on it only partially. Always double-check it from top to bottom. This is important for several reasons: it is ethically responsible as a practicing lawyer, helps avoid biases that algorithms might introduce, and ensures the work product is accurate and effective.
Having explored the general capabilities of generative AI for litigation attorneys, we can now delve into specific applications for each of the four areas mentioned earlier, starting with legal research.
Generating Fact Citations with Clearbrief
Locating and citing facts and evidence is crucial to any case, whether you’re working on a demand letter, pleading, memo, or correspondence. Sometimes, the correct fact can be challenging due to the sheer volume of documents to search, or you might need to know what’s available.
Traditionally, fact citation work has been manual and labor-intensive for attorneys, making it an ideal task for an efficient AI to tackle.
Clearbrief is highly recommended for generating fact citations and summaries. It is used by hundreds of law firms, courts, and agencies in the U.S. and was named the 2023 Litigation Product of the Year at Legalweek. Clearbrief is an effective tool for both solo practitioners and large law firms.
To use Clearbrief, highlight any fact sentence in a Word document and utilize the “find fact” cite function. Clearbrief’s specialized AI finds facts from discovery materials (documents and transcripts) with similar or related keywords and identifies related concepts in texts with different languages. Citations are automatically generated in the correct format and directly inserted into your Word document, with hyperlinks to the relevant document or transcript from discovery. Additionally, Clearbrief can compile exhibits and a Table of Authorities with hyperlinked citations.
Learn more about Clearbrief or schedule a demo.
Casetext’s CoCounsel and Legal Research
Legal research is an essential aspect of a litigation attorney’s work, requiring identifying controlling precedent in the relevant jurisdiction, additional supporting laws, and potential weaknesses.
Avoiding “hallucinations,” which can occur when generative AI is not used cautiously, is crucial in this context. Algorithms that create content may occasionally or frequently generate incorrect sources and facts, which is unacceptable for litigation attorneys in any setting.
Casetext’s CoCounsel is an excellent option in this regard, as users report that hallucinations are not a concern. Over 10,000 law firms utilize CoCounsel, which has a 4.8 out of 5 rating on G2 based on over 74 reviews.
By inputting the core legal issue, jurisdiction, and key facts, you’ll receive controlling precedent along with well-crafted arguments in a comprehensive research memo. Quoting and automatic citation in the correct format are also easily achievable.
In addition to legal research, CoCounsel offers other generative AI use cases, such as creating deposition outlines and drafting answers to complaints. Experience the benefits of Casetext’s popular CoCounsel by trying a free demo.
LexisAI and Enhanced Legal Research
As an advanced legal research tool, LexisAI offers unparalleled support to litigation attorneys seeking to optimize their research process. This powerful AI-driven platform comprehensively analyzes case law, statutes, regulations, and other legal materials, ensuring that attorneys have access to the most relevant and up-to-date information.
LexisAI eliminates the need to sift through countless documents manually, saving time and increasing efficiency. The platform’s AI algorithms identify pertinent legal authorities, highlight important passages, and suggest related materials that may strengthen your case or reveal potential weaknesses.
In addition to its core research functionality, LexisAI offers various features that support litigation attorneys throughout the entire case preparation process. These include drafting pleadings, generating deposition outlines, and creating answers to complaints, all with the precision and accuracy expected of a top-tier legal research tool.
LexisAI’s robust offerings make it a must-have tool for any litigation attorney seeking to stay ahead of the competition. To explore the full range of benefits LexisAI can provide, consider scheduling a demo or learning more about this cutting-edge platform.
Briefpoint and Discovery Responses and Requests
Drafting discovery responses is a crucial aspect of litigation work, but it can become monotonous when you already know what you want to say. For example, a response to a request for admissions may involve repeating the same objection multiple times.
As a litigation attorney, your valuable time would be better spent focusing on strategic planning rather than typing and double-checking for errors, which likely wasn’t your primary motivation for attending law school.
Software solutions like Briefpoint can alleviate this burden for California-based litigation attorneys. With a single browser login, you only need to upload the opposing counsel’s PDF. The Briefpoint platform supports most California documents.
Whether using a premade template or specialized AI, Briefpoint enables you to populate a page with the desired language, whether a response or an objection. Customers find the user interface intuitive and easy to use, allowing you to benefit from a no-cost demo quickly. If you prefer, you can learn more about our service before trying it out.
In addition to drafting discovery responses, Briefpoint offers features for preparing propounding discovery, including requests for admission, requests for production, and interrogatories. This comprehensive approach streamlines the entire discovery process, saving you time and effort while maintaining accuracy and consistency in your legal documents.
Test Briefpoint for yourself by scheduling a demo and starting a trial account.
Everlaw and Drafting Factual Statements
Using off-the-shelf tools like ChatGPT for generating legal writing is not recommended, as litigation attorneys require specialized software for their technical material.
If you use Everlaw to manage discovery, consider trying its drafting function, EverlawAI Assistant. Built-in safeguards prevent hallucinations from becoming an issue. Instead, Everlaw works based on your discovery evidence, including the documents it helped you locate.
This generative AI can provide a useful initial draft, whether you need a deposition summary or a fact-focused section for a brief. While you will ultimately edit the draft, having a fact-based starting point will help you reach the finish line. If you have yet to try Everlaw, consider a free demo.
Leveraging Generative AI in Litigation
Generative AI has significantly impacted various industries, including the legal field, and will continue to do so as the technology advances. While its use has both advantages and disadvantages, as discussed earlier, careful implementation and understanding of prompts can help manage the risks associated with generative AI without sacrificing competitive edge.
Ultimately, generative AI is an exciting new technology that skilled attorneys can handle effectively, just like any other risk or legal issue.
At Briefpoint, we specialize in automating repetitive aspects of discovery drafting, enabling litigation attorneys like you to focus on more profound thinking. We have witnessed our software’s benefits to clients and hope you experience similar advantages from the various technologies outlined in this article.
Practice Pointers: Written Discovery

Learn helpful best practices for drafting and using written discovery:
A litigation attorney must think and act in a strategic and measured way to be successful. If you are searching for practice pointers on how to create and handle written discovery in civil litigation, read this article to learn more.
Specifically, we will discuss:
Important first steps to prepare for the process of written discovery.
When to copy and paste or customize when drafting written discovery, and how to automate repetitive drafting tasks.
The importance of crafting clear and concise language and some tips for making that happen.
A set of best practices for three main types of written discovery requests, including not underestimating requests for admission.
How to best respond and object to discovery requests from the opposing party.
Read on.
Important first steps to prepare for written discovery
There are four, among other, important first steps that a litigation attorney should take when facing a discovery process.
Know the specific discovery rules that apply.
Do as much discovery as you can with your client.
Ask how written discovery will help you accomplish your goals.
Be realistic with your discovery timeline.
Know the specific discovery rules that apply
If you are in federal court, then the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure govern the discovery process. If you are in state court, then the civil procedure rules of that state apply. Important differences include, but are not limited to, the scope of permissible discovery requests and the number of interrogatories.
But those are not the only rules you have to study. Litigation attorneys should pay close attention to local district court rules. They sometimes hold different views even when interpreting the same rules of civil procedure.
Do as much discovery as you can with your client
Discovery for your case starts during intake. From the beginning your client is the best starting point for relevant information, evidence, witnesses, and documents. Talk to your client about what they need to do to help you propound and respond to discovery.
Ask how written discovery will help you accomplish your goals
Your own efforts to investigate the case help you know what the opposing party or a third party may have that you want to target during the discovery process. Think carefully about what type of information each source may have. At times, the answers might be unexpected. Because you never want to ask questions whose answers you don’t know at trial, the time to find the answers to your case’s critical questions starts with discovery.
In general, if you believe that asking for something might help your client, ask for it. The scope of what is admissible at trial is narrower than what you can put into the discovery process.
Garnering relevant facts and helpful information is only one goal you may have for written discovery. Other objectives can include testing the pleadings. Whatever you do, make sure you can provide support your decisions if necessary. In general, the rules of discovery consider the needs of the case as well as prejudice and negative impact on the parties involved. The more you understand the discovery needs of your client and the alternatives available, the better off you will be during – for example – motion practice.
Be realistic with your discovery timeline
Make a discovery timeline. Tailor it to the circumstances of your client and the case. Your discovery timeline should account for written discovery between the opposing parties as one aspect of a broader discovery process.
As an example, some cases may require third-party discovery via subpoenas. You may decide that depositions and documents with third parties would also be valuable. Understanding that third-party discovery can take a significant amount of time to execute is critical for you timeline – it may take you weeks to discuss and come to terms with third parties regarding their deposition dates and document productions.
Drafting written discovery: Copying, customizing, and automating
Use pre-approved discovery requests as much as you can
Use discovery requests that have been pre-approved in your jurisdiction. Depending on the jurisdiction, this could include, but may not be limited to, interrogatories asking for basic information and requests for admission seeking to admit the genuineness of documents. It will be difficult for the opposing party to objects on grounds of ambiguity or burden given the judicially-approved nature of the form interrogatories.
Tailor discovery requests to the case at hand
The more litigation experience that you have under your belt, the more you will encounter situations where you know exactly what information you need to win your case.
Until then, be as thoughtful as you can when drafting requests or interrogatories. Copying and pasting from discovery requests made by other practitioners can be a waste of your time and your client’s money because each case involves a unique nexus of facts. That being said, by evaluating the complaint and answer underlying sample discovery requests will be much more helpful because you’ll be able to determine what requests relate to what theories/facts.
Use software to save time on routine work
Options for software in the legal industry have improved significantly in recent years. This is especially true with the rise of artificial intelligence. Attorneys have access to great tools. The best legal industry software saves attorneys time on routine work. Litigation attorneys also have access to useful technology. Software can automate litigation tasks. This includes drafting discovery response documents.
Briefpoint, for example, automates the construction of discovery response documents.
Craft clear and concise language
Use clear and concise language as much as you can. Written discovery requests and responses should be technical – not inflammatory. Make your arguments in motions and in court – discovery requests are not the place to postulate the merits of your case.
Standard English
Use standard English. Avoid legalese to the extent possible. If your discovery requests are shown to a jury, they will respond much better to simple, easy-to-understand language. This will be important if, for example, you use a request for admission response for purposes of impeachment via cross-examination. And it’s not just the jury who will appreciate simpler word choice and shorter sentences. The judge will too. Further, the more clearly you write, the less grounds for objection based on ambiguity.
Use definitions
If a term in your written discovery is ambiguous, either substitute it for clearer language or define the term. Depending on your jurisdiction, terms may be required to bein a centralized index or within each request or interrogatory wherein the defined term is used.
Avoid intricate subparts and multiple “and/or” operators
Written discovery requests can run into problems in two ways, among others. One, using subparts in written interrogatories and requests for admission. Two, multiple “and/or” operators. Both can create confusion and will ultimately expose your requests or interrogatories to objection. Keep your requests from becoming intricate. Try splitting the sentences or subparts into multiple questions.
Refer to the pleadings
When drafting discovery requests, refer to the pleadings. Paying close attention to them while you draft will keep you focused on the most important questions. Additionally, the more you can use opposing counsel’s own words in your requests/interrogatories, the less grounds they’ll have for objecting on ambiguity or relevance.
Discovery requests
Let’s discuss three important types of written discovery requests:
Written interrogatories
Requests for admission
Requests for Production
Keep reading.
Interrogatories
Interrogatories are helpful tools for a variety of reasons, often for identifying and organizing facts including, but not limited to, the identification of witnesses and locations where evidence is stored.
You may find, however, that interrogatory answers from the opposing party are scripted and less helpful than documents related to your case’s fact pattern.
You will elicit answers from the opposing party that counsel likely played a substantial role in creating. Opposing counsel will also likely use their answers to your interrogatories to prepare their witnesses before testimony. You should do the same with the answers to interrogatories that you worked on.
Try the “interrogatory first” approach
Before propounding a document request, consider a propounding interrogatorries first. This is suggested because it tends to make the responding party’s production of documents more orderly for the requesting party. You would first propound interrogatories that ask the opposing party to identify documents. Then, after reviewing answers to those interrogatories, you would send a request for production of documents for the documents they identified.
Contention interrogatories
Contention interrogatories will elicit answers from the responding party that may reveal the evidence and witnesses they will use to support their claims and undermine yours. Use of contention interrogatories may lead to objections, including of privilege. The opposing party’s counsel may object that it would be premature to answer the interrogatory. Eventually they will have to answer.
Requests for Production of Documents
Document discovery is potentially the most critical function of discovery. Requests for production of documents can elicit some of the strongest evidence in a case. Contemporaneous documents can offer a real-world, unscripted view into the facts of your case – unfiltered by the motives of your opposing counsel.
Try not to propound broad document requests without first understanding what you’re looking for. Instead, focus on crafting tailored document requests based on what you know about the case so far. These requests will lead to useful documents and you will appear more defensible should you find yourself compelling responses.
Requests for admission
Requests for Admissions have numerous benefits, which we will discuss after technical writing pointers.
Tips for when you draft requests for admission
Your requests for admission should be as carefully written as you can make them. Clear communication avoids confusion and prevents some obfuscation. Better writing is a ward against valid objections.
The language in your requests for admission should satisfy, among others, two criteria. First, write clearly: State the fact you want admitted. Second, tailor the language: State no more facts than what you want admitted; there is one fact described in the request.
Tips to write clear requests for admission:
Do not use adjectives.
Use plain words.
Avoid clauses as much as you can.
Strive to make the request one simple sentence.
Try not to rely on a definitions section to carry your burden. Definitions can help make drafting more efficient, but they can also become clunky and make reading difficult. Consider using helpful and simple language in parentheticals after a potentially ambiguous word. It is meant to be cited as it is written, with no additional aid needed to understand it.
Use requests for admission to settle uncontroversial facts
Requests for admission settle issues and provide some finality so the parties can focus on more important issues of fact. You are unlikely to get an admission of a highly-disputed fact (buy you should still try).
Depositions and cross examination
You can use an admission to take previously garnered deposition testimony and make it more firm.
An admission can be useful later on for cross examination because they are easy to quote.
If the opposing party has been evasive with interrogatories or production of documents, try a request for admission before depositions to make it so they can’t claim confusion. The opposing party has been focused on the key issues.
Three more ways to use requests for admission
Propounding requests for admission early in the discovery process may help you discover holes in the opposing party’s argument and buffer your own.
Requests for admission can help you figure out what exactly the opposing party is disputing factually.
You can send a request for admission near the close of discovery to admit facts for a motion for summary judgment or to help with negotiations to settle the case.
Responding
Objecting to written discovery requests
Objections are common during the discovery process. When objections are raised during the discovery process, parties in the majority of jurisdictions have to discuss the dispute (“meet and confer”). Be prepared to handle motion practice, as it is common when parties stand on their objections.
Telling the truth and advocating at the same time
When you do respond and answer discovery requests, make sure two things are true.
The words directly address the request and they state the truth.
You answered and gave no more than you needed; you stayed within the scope of the request.
At the same time, you are an advocate. If possible, frame the response with context that favors your client’s position. For example, consider a written interrogatory is a closed-ended question calling for a “no” or a “yes” and you want to say no, say no and then explain why. Tell the story. Whenever the opposing party’s counsel tries to use your response, your client’s side of the story is there too.
Answering written interrogatories
Learn two practice pointers for answering written interrogatories in civil cases.
First, draft every interrogatory answer knowing that any inconsistencies will be used for impeachment. Make sure that you and the witness are fully comfortable with the answer ahead of time.
Second, it can be difficult and costly to respond to interrogatories asking for identification of documents. A failure to identify documents may be acceptable, though regrettable, if the interrogatory is broadly framed or answering the interrogatory fully is burdensome.
Responding to requests for admission
Be reasonable when you respond and object to requests for admission. If the fact matters in some way and it’s not something you can really disagree with, admit it. If you agree with part but not all you may be required to state that in your response (depending on the jurisdiction).
If you deny a request for admission, then in federal courts and in California, among other jurisdictions, you could potentially be forced to pay the opposing party’s expenses incurred to prove the fact. Federal Rules of Civil Procedure 37(c)(2); California Code of Civil Procedure § 2033.420.
Make drafting written discovery responses easier
Written discovery is part of what litigation attorneys do. It has its own learning curve but, with enough time and practice, drafting discovery will become second nature.
If this article gave you helpful practice pointers, consider if there is room to automate the drafting of your discovery response documents. A free demo of Briefpoint’s software is an easy way to see how much time you will save: Schedule a Demo.
DISCLAIMER: THIS IS NOT LEGAL ADVICE AND BRIEFPOINT IS NOT AN ATTORNEY.
IF YOU ARE SEEKING ASSISTANCE IN SELF-REPRESENTATION, SEEK COUNSEL.