21 Must-Have Apps for Lawyers in 2026
21 Must-Have Apps for Lawyers in 2026
Most law practices don’t fall behind because of complicated legal questions. They fall behind in the space between tasks.
For example, notes get saved in one place, drafts in another, time entries somewhere else. None of it is dramatic on its own, but over the course of a week or a month or even a year, those small inefficiencies quietly eat into your focus.
Fortunately, a well-chosen set of apps can help smooth that out. The right tools reduce the back-and-forth, keep your work connected, and give you a clearer view of what’s moving and what needs attention.
Below are 21 apps that genuinely support the way lawyers work today. Some are built specifically for legal practice, others are broader productivity tools that fit naturally into a legal workflow. But each one earns its spot for a reason.

What Are Legal Apps?
Every industry has its core tools. Designers rely on creative software. Accountants use financial platforms. Sales teams live inside CRMs. Lawyers have their own category of apps built around the structure and pressure of legal work.
Legal apps are software tools shaped by how a law practice actually operates. They account for deadlines that carry real consequences, detailed documentation requirements, and the need for organized task management under constant time constraints.
While many industries focus on speed and volume, legal work demands accuracy, traceability, and controlled workflows.
As mentioned, some legal apps are purpose-built for firms. Others come from broader productivity categories and adapt well to legal environments.
What separates them from generic business tools is how they support work productivity without disrupting professional standards or compliance needs.
How Can These Apps Benefit Law Firms and Legal Professionals?
You already know where most of your time goes. It’s not always the hard legal questions. Often, it’s the follow-ups, the tracking, and the small administrative tasks that sit between you and the actual work.
Legal apps are there to help clean that up. Essentially, they give your day more structure, so you’re not relying on memory or scattered systems to keep things moving.
When work is organized properly, you don’t have to think twice about what’s next or where something lives.
Here’s what that can look like:
- Fewer administrative tasks: Routine steps take less effort, which frees up mental space.
- Better control over important documents: Files stay connected to the right matters and are easier to locate.
- Real-time collaboration: Your team sees updates as they happen and stays aligned.
- Clearer coordination in larger firms: Responsibilities and workloads are more visible.
- Artificial intelligence support: Legal drafting and review move faster while you stay in charge.
- Stronger work productivity overall: Less friction means more consistent progress.
21 Best Apps For Lawyers
There are tons of tools out there, but not all of them are built with lawyers in mind. We’ve rounded up some of the most useful apps (both legal-specific and general productivity tools) that actually make a difference in your day-to-day work:
1. Briefpoint

Discovery has a way of taking over your calendar. One large set of RFPs can eat up days, especially when court dates are tight, and your team is already stretched. Briefpoint was built for that exact pressure in the legal world.
It’s an AI-powered discovery platform that helps you propound and respond to requests for production, requests for admission, and interrogatories in a fraction of the usual time.
With its Autodoc feature, you can upload a complaint, RFPs, and production files, then generate captioned Word responses with page-level Bates citations in minutes. What used to take 30–40 hours can now take minutes.
Briefpoint works for both small firms and larger litigation teams. The user-friendly interface means there’s no heavy setup, and it integrates with tools like Clio, Smokeball, and MyCase. It’s SOC 2 Type II certified, HIPAA compliant, and available in all 50 states and federal courts.
More than 1,500 law firms use Briefpoint, with an average 4.9 satisfaction rating. Plus, attorneys regularly report saving 30+ hours per case.
Key Features
- Propound discovery from complaints: Generate up to 70 targeted, objection-aware requests in minutes.
- AI-assisted response drafting: Apply consistent objections and draft answers quickly.
- Autodoc production packages: Create Bates-numbered productions with cited Word responses.
- Client response collection portal: Send plain-English questions and receive Word-ready drafts.
- Security and compliance: SOC 2 certified, HIPAA compliant, encrypted data.
Want to learn how Briefpoint can fit into your workflow? Book a demo today!
2. Evernote
Evernote is a simple note-taking app that helps you keep everything in one place, such as case notes, client information, meeting summaries, to-do lists, and even voice memos.
You can tag, search, and organize your notes into notebooks, which helps make it easy to find what you need fast.
Source: Evernote.com
Key Features
- Cross-device syncing: Access your notes from desktop, tablet, or phone without losing updates.
- Flexible note formats: Create text notes, attach images, or record audio in one place.
- Organized notebooks and tags: Sort information in a way that fits your workflow.
- Powerful search: Quickly locate saved notes using keywords and filters.
3. Clio
Clio is a case management platform designed specifically for the legal world. It brings your files, legal billing, scheduling, and client communication into one system so your practice runs with fewer moving parts.
Source: G2
It works well for solo attorneys and growing firms alike, especially if you want clearer visibility into deadlines, workloads, and client messages without relying on disconnected tools.
Its built-in calendar app, billing tools, and matter tracking features help boost productivity by keeping everything tied to the right case.
Key Features
- Centralized case management: Organize matters, contacts, and documents from a single dashboard.
- Integrated calendar app: Track court dates, meetings, and deadlines alongside your cases.
- Billing and time tracking: Log hours and generate invoices directly within the platform.
- Secure client portal: Share files and client messages in a protected environment.
- Wide integrations: Connect with tools like Outlook, Zoom, and Dropbox for smoother workflows.
4. OneDrive
OneDrive is Microsoft’s cloud solution and a practical choice for lawyers who already work inside the Microsoft ecosystem.
It keeps case files and other files stored in one secure location while allowing you to open, edit, and share the same document without worrying about version confusion.
Source: G2
Because it connects directly with Word, Excel, and Outlook, your files stay synced automatically. That makes it easier to collaborate, store drafts, and keep everything backed up. There’s also a free plan available, which can work well for smaller practices getting started.
Key Features
- Cloud storage with automatic syncing: Keep case files and other files updated across devices.
- Real-time access to the same document: Collaborate without creating duplicate versions.
- Microsoft Office integration: Open and edit files directly in Word, Excel, and Outlook.
- Flexible sharing controls: Grant access to clients or colleagues with permission settings.
- Cross-device availability: Access files from desktop, tablet, or mobile phones.
5. Google Docs
Google Docs is a simplistic tool, but that’s part of what makes it so useful. It’s quick to open, easy to use, and perfect for drafting documents with other lawyers or clients. You can leave comments, track changes, and never worry about hitting “save.”
Source: Docs.Google.com
Key Features
- Real-time editing and collaboration: Work on the same document simultaneously with comments and suggestions.
- Automatic saving to Google Drive: Changes are saved instantly without manual backups.
- Flexible sharing controls: Set viewing, commenting, or editing permissions for each user.
- Cross-device access: Open and edit documents from desktop, tablet, or mobile devices.
6. Clockify
Clockify is a simple time-tracking app that helps you log billable hours without much setup. It’s great for solo lawyers or small teams who want something quick and easy. You can track time by client, case, or task and generate clean reports when it’s time to bill.
![]()
Source: G2
That said, it may be too simple for larger law firms that need more advanced billing features or deep integrations.
Key Features
- One-click timer and manual entry: Start tracking instantly or log hours after the fact.
- Client and case tagging: Assign time entries to specific matters or tasks.
- Detailed reporting tools: Generate summaries for billing and internal review.
- Multi-platform access: Use on web, desktop, or mobile devices.
7. Adobe Reader
Adobe Reader is a must-have since many legal documents come in PDF form. It allows quick viewing, highlighting, commenting, and signing without printing anything.
Source: G2
Legal professionals can easily review and send legal documents while keeping everything digital and organized.
Key Features
- PDF viewing and annotation: Highlight, comment, and mark up documents directly within the file.
- Form filling and e-signatures: Complete and sign PDF forms without printing.
- Cross-device compatibility: Access and review files on desktop or mobile.
- Adobe ecosystem integration: Connect with other Adobe tools for editing and document workflows.
8. Grammarly
Grammarly helps catch grammar errors, awkward phrasing, and tone issues before anything is sent out. In the legal industry, clear writing matters, and this tool makes it easier to get things right the first time.
Source: G2
Plus, it works in email, documents, and even web browsers, which helps improve productivity across the board.
Key Features
- Real-time grammar and spell check: Identify errors as you write.
- Tone and clarity feedback: Adjust phrasing to match a professional voice.
- Cross-platform support: Works in Google Docs, email, and browser-based tools.
- Custom writing settings: Set preferences for formal or firm-specific standards.
9. Dropbox
Dropbox is a reliable file storage app widely used in the legal profession for sharing and organizing documents. It offers free storage to get started and makes accessing files from any device simple.
Source: G2
It integrates smoothly with common workplace tools, so it can fit into your existing setup without requiring major changes.
Key Features
- Cloud storage with device syncing: Keep files updated across desktop, mobile, and web.
- Secure file sharing: Control access with customizable permission settings.
- App integrations: Connect with tools like Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Office.
- Anywhere access: Open and manage documents from multiple devices.
10. Zapier
Zapier is a great tool for busy lawyers who want to cut down on repetitive tasks. It connects different apps and lets them work together automatically.
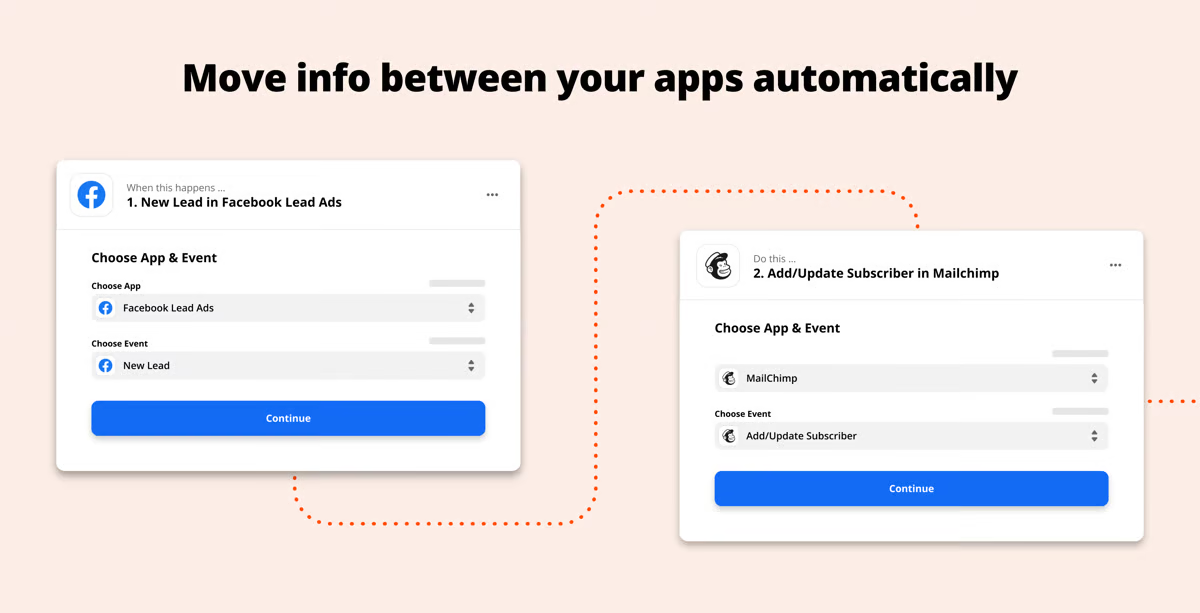
Source: G2
For example, you can set it up so that every time you receive a signed document in Dropbox, it gets copied to a case folder in Google Drive, and you get an email alert without doing anything manually.
By setting up these “Zaps” (which are basically if-this-then-that rules), you can streamline legal workflows and save a lot of time. It also works with thousands of apps, so chances are it fits right into how you already work.
Key Features
- App-to-app automation: Connect tools like Gmail, Google Docs, Clio, and Dropbox to run tasks automatically.
- No-code setup: Create workflows using simple trigger-and-action rules.
- Custom workflow rules: Automate document routing, alerts, and status updates.
- Wide app compatibility: Integrates with thousands of business and productivity platforms.
11. Slack
Slack is a messaging app that helps legal teams communicate quickly and easily. You can set up channels for different cases or departments and keep all your conversations organized. It’s easy to share files, ask quick questions, and get real-time updates.
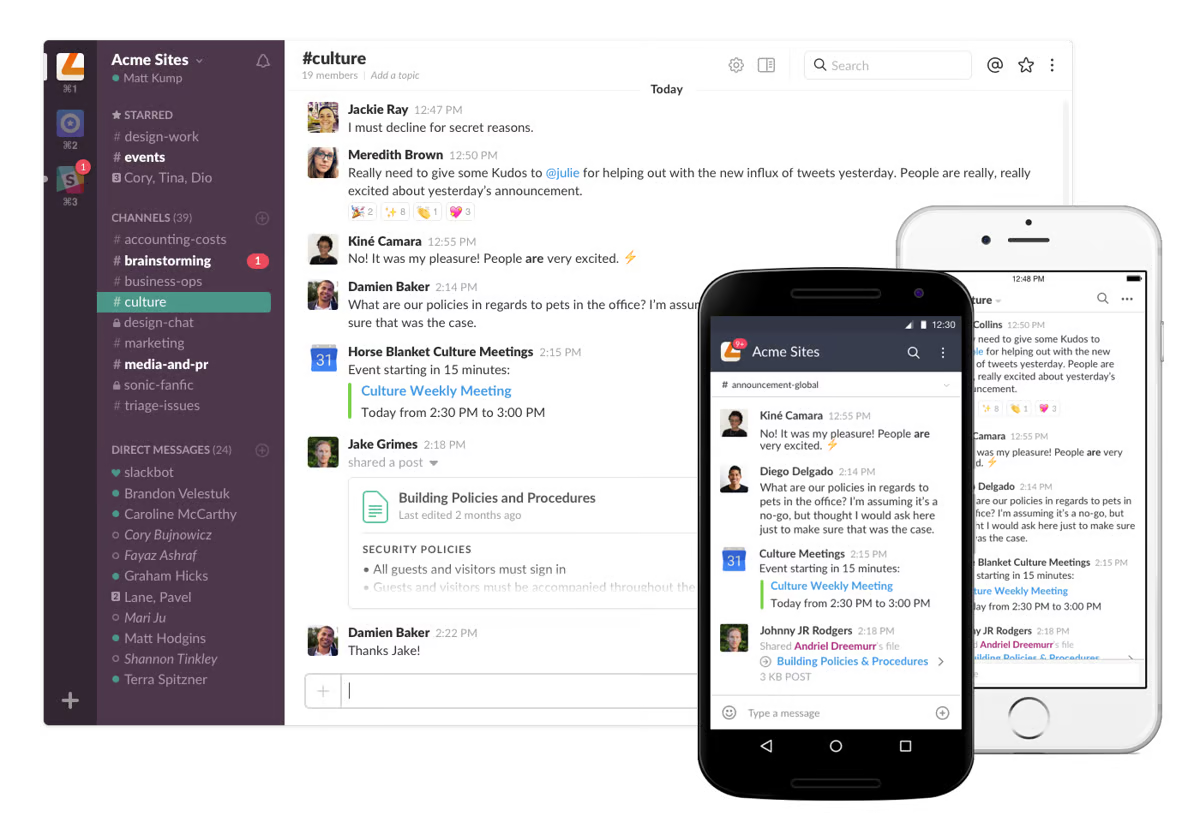
Source: G2
Key Features
- Channel-based messaging: Organize conversations by case, team, or topic.
- Direct messaging: Communicate privately with colleagues when needed.
- Searchable message history: Quickly find past discussions and shared files.
- Cross-device access: Use on desktop and mobile without losing updates.
- App integrations: Connect with tools like Google Drive, Zoom, and Calendly.
12. QuickBooks Online
QuickBooks Online is a cloud-based accounting platform that many law firms use to manage their finances in one place.

Source: G2
It covers billing, expense tracking, reporting, and payment processing without requiring a complicated setup. The layout has a simple interface, which makes it easier to navigate even if accounting isn’t your focus.
It works well for solo attorneys and small to mid-sized firms that want clearer visibility into revenue, outstanding invoices, and overall cash flow. You can attach detailed notes to transactions, categorize expenses, and connect your bank accounts for automatic updates.
Key Features
- Invoicing and online payments: Send invoices and accept online payments directly from clients.
- Integrated payment processing: Manage credit card and ACH transactions within the platform.
- Time tracking tools: Log billable hours and convert them into invoices.
- Expense tracking with detailed notes: Attach receipts and add context to each transaction.
- Set reminders: Automate payment reminders to reduce follow-ups.
- Mobile access and digital wallet support: Monitor finances and track payments on the go.
13. Toggl Track
Toggl Track is a time-tracking app built for professionals who want clarity without a complicated setup.
It’s especially helpful if you’re balancing multiple clients, matters, or internal tasks and want a cleaner picture of how your hours break down.
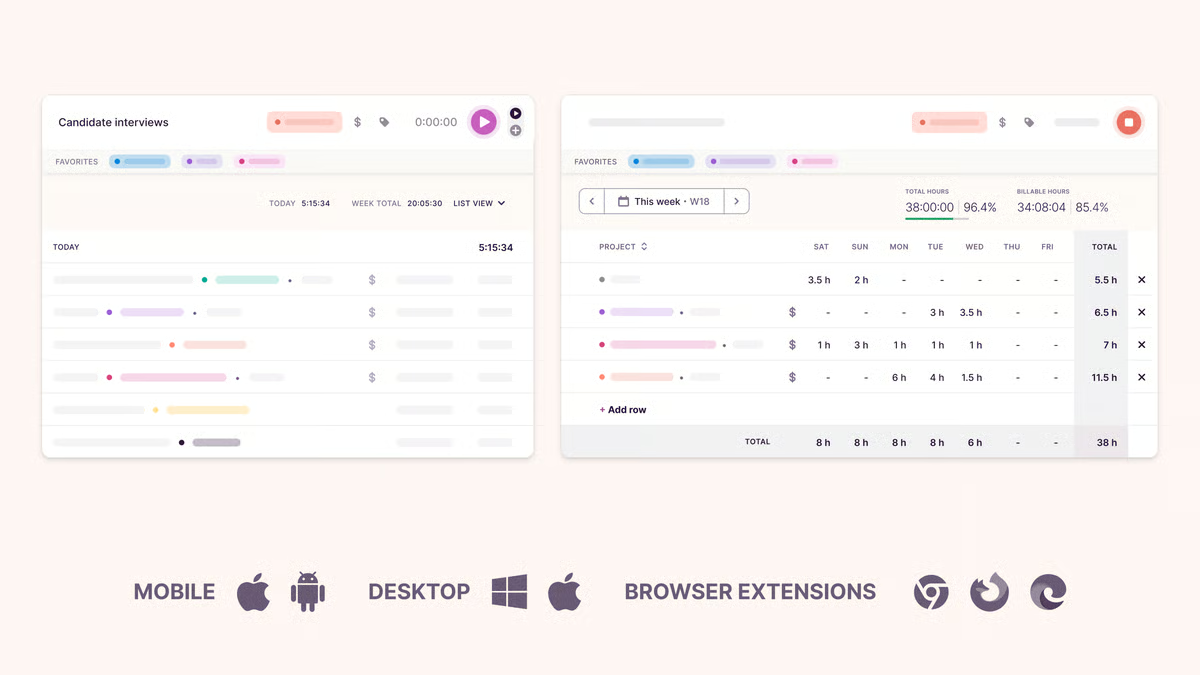
Source: G2
The layout is also straightforward, so logging time doesn’t feel like another chore at the end of the day.
Key Features
- One-click timers and manual entry: Start tracking instantly or log time after completing a task.
- Client and matter tagging: Assign hours to specific cases or projects for better organization.
- Clear reporting tools: Generate easy-to-read summaries of billable and non-billable time.
- Multi-platform support: Available on desktop, mobile, and browser extensions.
14. Zoom
Zoom has become a standard meeting platform for many professionals, including those in the legal world.
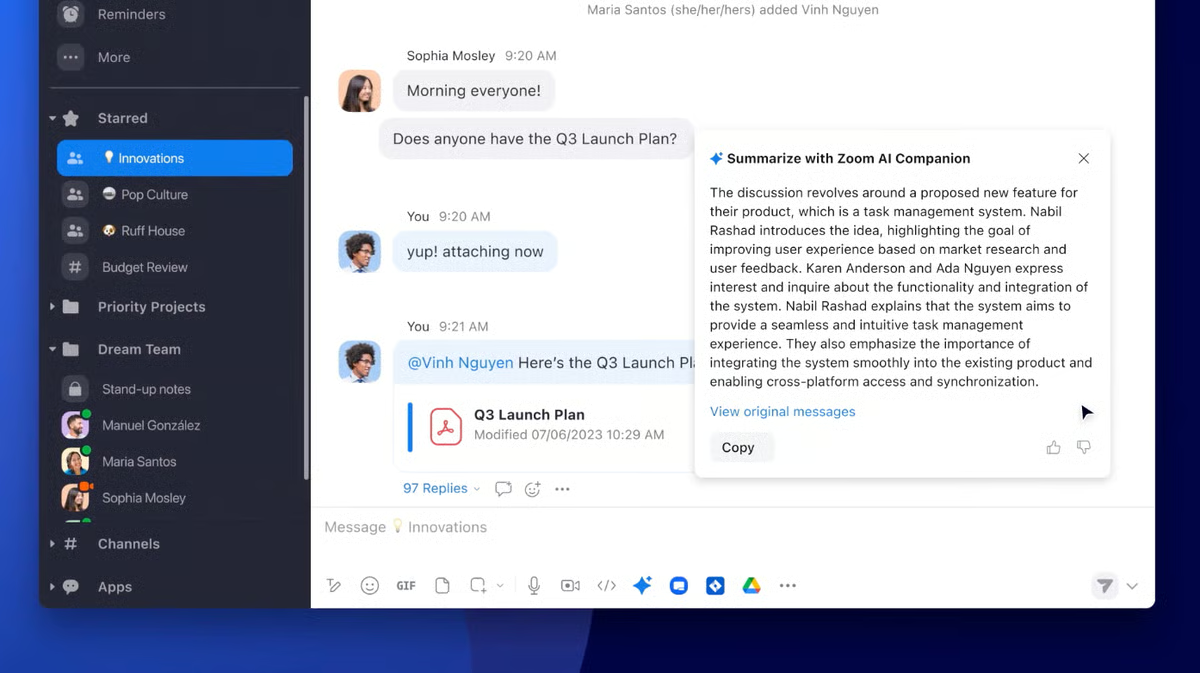
Source: G2
It supports virtual client meetings, internal team discussions, and remote appearances when needed. The setup is straightforward, and joining a meeting typically takes only a link and a few clicks.
It works reliably across devices, which makes it practical for firms coordinating across offices or time zones.
Key Features
- High-quality video and audio: Stable calls for client meetings and team discussions.
- Built-in scheduling tools: Coordinate meetings with calendar and time zone support.
- Screen sharing and recording: Present documents and save sessions when needed.
- Cross-platform access: Available on desktop and mobile devices.
15. Otter.ai
Otter.ai is a transcription tool that turns spoken conversations into searchable text. It’s useful for lawyers who want a written record of meetings, phone calls, or other audio recordings without taking manual notes the entire time.
Source: G2
You can record directly inside the app or upload existing audio files, and the transcript appears within minutes. The interface is straightforward, which makes it extremely easy to review conversations, highlight key sections, and share notes with your team.
It works well for internal meetings, client discussions, and strategy sessions where capturing details matters.
Many users consider it a great app for organizing spoken information in a way that’s actually usable later.
Key Features
- Automatic transcription: Convert phone calls and audio recordings into searchable text.
- Live recording and uploads: Record in-app or import existing audio files.
- Searchable transcripts: Find keywords quickly within long conversations.
- Collaboration tools: Highlight, comment, and share transcripts with your team.
- Cross-device access: Use on desktop or mobile devices.
16. Feedly
Feedly is a smart news reader that helps lawyers stay updated on legal trends, case law, and industry news, all in one place. You can follow blogs, court updates, news sites, and even YouTube channels, then read them in a clean, organized feed.
Source: Feedly.com
It’s a great way to cut down on time spent checking multiple websites. Feedly also lets you group your sources into categories, so you can quickly scan updates on specific topics like litigation, privacy law, or tech news whenever you have a free minute.
Key Features
- Custom news feeds: Follow legal blogs, court updates, and industry sources in one place.
- Organized categories: Group content by topic for easier scanning.
- Clean reading interface: View articles in a distraction-free layout.
- Web and mobile access: Check updates from desktop or mobile devices.
- Sharing and saving tools: Send articles to your team or bookmark for later reference.
17. LastPass
LastPass is a secure password manager that helps legal professionals keep their login information safe and organized.
Source: G2
Instead of writing down passwords or reusing the same ones, you can store them all in one secure vault. Just remember one master password, and LastPass handles the rest.
It’s a smart way to protect sensitive client data and save time when jumping between tools.
Key Features
- Secure password vault: Store and autofill login credentials across websites and apps.
- Password generator: Create strong, unique passwords for each account.
- Secure sharing options: Share credentials safely within your team.
- Cross-platform support: Works on browsers, desktop applications, and mobile devices.
18. Calendly
Calendly takes the back-and-forth out of scheduling by letting others book time with you based on your availability. It’s a good app for lawyers managing client meetings, and it’s also a good tool for law students coordinating study groups or interviews.
Source: G2
The app works smoothly on desktop, iOS, and Android devices, which makes it easy to manage your schedule from anywhere.
Key Features
- Self-service scheduling: Allow clients and colleagues to book meetings based on your availability.
- Automated reminders: Send calendar invites and email confirmations automatically.
- Calendar integrations: Sync with Google Calendar, Outlook, and Zoom.
- Cross-device access: Manage bookings on desktop, iOS, and Android devices.
19. Asana
Asana is a task and project management app that helps law firms organize work and keep track of who is responsible for what. It allows you to break cases into smaller steps, assign tasks, and monitor deadlines in one shared space.
Source: G2
Key Features
- Custom workflows: Create task lists and timelines tailored to each matter.
- Task assignment and deadlines: Assign responsibilities, add notes, and set due dates.
- Multiple project views: Track progress using boards, calendars, or list views.
- Cross-platform access: Stay updated on desktop and mobile devices.
20. ChatGPT
ChatGPT is an AI app that can help with writing, research, brainstorming, and even reviewing legal language.
While it’s not designed specifically for legal professionals, many lawyers use it to speed up routine tasks like drafting emails, rewording documents, or summarizing long content. It can be a handy assistant as long as it’s used with care.
Source: ChatGPT.com
An internet connection is required to use it, and it’s best treated as a support tool, not a replacement for legal judgment.
Key Features
- Content drafting and editing: Generate, rephrase, and summarize written material.
- Question answering: Provide explanations and quick research support.
- Brainstorming assistance: Help outline ideas or refine arguments.
- Web and mobile access: Available through browser and mobile apps.
21. Google Calendar
Google Calendar is one of the favorite apps lawyers rely on to keep deadlines, meetings, and court dates organized in one place. It offers a simple way to schedule appointments, block focused work time, and avoid double-booking.
Source: Indeed.com
Because it connects easily with email and other productivity tools, creating a calendar event often takes just a click. You can also share calendars with colleagues or assistants, which makes coordination smoother inside growing firms.
Key Features
- Quick event creation: Add a calendar event directly from email or within the app.
- Easy scheduling: Schedule appointments with built-in availability visibility.
- Shared calendar access: Share calendars with team members for better coordination.
- Cross-platform support: Use on desktop, mobile, and tablet devices.
Start Automating Your Discovery Documents Today
The point of this article was simple: lawyers don’t need to do everything the hard way.
With the right apps, staying organized, saving time, and keeping your practice running smoothly is actually possible. From note-taking to time tracking to team communication, there’s a tool that fits the way you work.
But if there’s one task that still eats up too much of your day, it’s drafting discovery documents.
Briefpoint can make a real difference. It’s built specifically for lawyers who want to cut hours of drafting down to just minutes without sacrificing quality or control.
If you’re ready to spend less time formatting and more time lawyering, give Briefpoint a try.
FAQs About Apps For Lawyers
What apps are good for law?
Good apps for law usually support practice management, document organization, time tracking, and communication. Many lawyers combine legal-specific platforms with general productivity tools to create a setup that fits their workflow.
What is the 80/20 rule for lawyers?
The 80/20 rule suggests that a small portion of tasks or clients often generate most of the results. In practice, this can mean focusing more attention on high-value work while using tools to handle lower-value administrative tasks.
Which AI is best for lawyers?
The best AI tool depends on the task. Some tools focus on drafting and research, while others support discovery or contract review. Many offer a free version with optional paid plans for advanced features.
Are there free apps lawyers can use to get started?
Yes. Many tools offer a free version before upgrading to paid plans. These can include time tracking, document editing, and even basic client intake features. Free tiers are often useful for testing a new app before committing.
Can apps help with scheduling and collaboration?
Yes. Many tools let you schedule appointments, create a calendar event automatically, and share calendars with your team. Others support seamless collaboration on documents and even basic web pages for client intake and communication.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
A Guide to eDiscovery for Law Firms In 2026
A Guide to eDiscovery for Law Firms In 2026
How much of your discovery time goes into legal thinking, and how much goes into managing files?
For most law firms, digital information now drives discovery, and keeping that material organized can feel like a job of its own.
In 2026, the upside is that eDiscovery gives you a structured way to handle that digital work. With cloud-based eDiscovery tools, files move through collection, review, and production without relying on manual tracking or disconnected systems.
This means the process stays clearer, and discovery work becomes easier to manage as cases move forward.
Below, we look at how law firms approach eDiscovery in practice and how those choices shape the discovery process.
What Is eDiscovery?
eDiscovery, or electronic discovery, is how legal teams manage digital information during the discovery process.
Emails, shared documents, chat messages, cloud files, and even data pulled from apps all come into play. If the information lives on a screen, eDiscovery is usually part of the conversation.
Traditional discovery looked very different. Paper files, boxes of records, and manual review were the norm. That setup made sense when evidence almost always stayed physical.
Now, most case-related information is digital, and trying to handle it the old way quickly becomes messy and time-consuming. The eDiscovery process grew out of that shift to give legal teams a clearer path for handling digital material from start to finish.
At a high level, the eDiscovery process includes:
- Identifying digital data tied to a matter
- Preserving relevant information
- Collecting files from different systems
- Reviewing materials for relevance and privilege
- Producing responsive documents
In other words, the purpose remains familiar. eDiscovery helps legal teams manage digital evidence in a way that supports the broader discovery process, but without turning every case into a manual sorting exercise.
Common Problems in Manual Discovery Processes
Manual discovery is familiar to most legal professionals, but it often creates friction once a matter starts moving. As legal proceedings rely more on digital files, manual processes can feel harder to keep under control than expected.
Here are some common issues that come up:
- Digital files end up scattered: Emails, shared drives, and local folders all hold pieces of the record, which makes it difficult to see what’s been collected, reviewed, or produced.
- Discovery costs increase over time: Manual review takes longer, and those hours add up. Discovery costs often grow as the case progresses, sometimes without a clear way to track such expenses.
- Limited visibility into the work: Teams often rely on spreadsheets or informal updates to track progress, which makes it easier for steps to be missed or repeated.
- Inconsistent review decisions: Without shared tools or legal workflows, relevance and privilege calls can vary between reviewers, leading to additional review work later.
- Greater risk of mistakes: Manual handling increases the chance that files are overlooked or productions are incomplete, which can create problems during legal proceedings.
- Difficulty with cost recovery: When time and effort aren’t clearly documented, cost recovery for discovery work becomes more difficult.
How Law Firms Handle eDiscovery Today
Most law firms rely on a mix of tools, people, and outside help to get discovery done. The setup varies by case size, budget, and internal resources, but a few common patterns show up again and again:
In-House Review Teams
In-house review teams are made up of attorneys, paralegals, and support staff within legal firms who handle document review as part of their regular workload. These teams review electronic documents tied to active matters, flag relevance, assess privilege, and prepare materials for production.
Because they already understand the case strategy and client context, reviewing documents often feels more integrated with the rest of the litigation work.
Compared with external teams, in-house reviewers offer tighter control and faster feedback loops. Questions get answered quickly, and adjustments happen without formal handoffs.
The tradeoff usually shows up in capacity. When data volumes spike or deadlines tighten, internal teams can get stretched thin, especially if document review competes with other responsibilities.
On the other hand, external review teams bring scale and dedicated focus, which can help with large productions. Still, in-house teams tend to work best for ongoing matters, targeted review sets, or cases where familiarity with the facts matters as much as speed.
Outside eDiscovery Vendors
Outside eDiscovery vendors are specialized third-party providers that support law firms with parts of the e-discovery process, such as data processing, document review, production prep, and analytics.
These vendors bring scale, dedicated teams, and tools that many firms can’t justify owning in-house, especially on big cases where the volume of electronic documents and complexity can overwhelm internal resources.
It may be comforting to know that the market for outsourced legal services is growing fast. The global legal process outsourcing space was valued at USD 23.45 billion in 2024, which shows strong growth as firms look to manage cost and workflow pressures.
Some benefits of working with vendors include:
- Expanded capacity for large document review sets
- Access to expert e-discovery teams and tools
- Faster data processing and defensibility tracking
- Flexible resourcing tied to case needs
- Reduced pressure on internal staff
Outsourcing can be especially appealing when deadlines tighten or when cases involve massive volumes of digital data.
Hybrid Discovery Models
Hybrid discovery models are what many firms land on once they’ve lived through both extremes.
You keep some discovery work in-house, and you bring in outside help when volume or timing makes that necessary. It’s less a formal system and more a flexible way to handle electronically stored information without overwhelming your own team.
Typically, internal attorneys stay close to the case. They decide what counts as relevant documents, handle privilege calls, and make judgment-heavy decisions.
Outside resources step in for data processing, large review sets, or technical tasks that benefit from scale and specialized legal technology.
The appeal is control without burnout. You stay connected to the substance of the matter while letting an eDiscovery solution handle the heavy lifting.
Plus, as cases grow or shrink, the model adjusts with you to make it easier to manage shifting discovery demands without constantly reworking your setup.
Cloud-Based Platforms
Cloud solutions have become the default for how most legal teams handle discovery today. These systems let you collect documents, review electronic data, and manage production from one shared environment.
Teams can log in from anywhere, collaborate in real time, and move between matters without juggling multiple platforms.
Non-cloud systems still exist, but they’re far less common now unless a law firm or legal team is holding onto truly archaic practices.
Those setups usually depend on on-prem servers, manual transfers, and limited access, which slows everything down once data volume increases or deadlines tighten.
Cloud tools remove much of that friction. They scale as matters grow, support modern data sources, and keep everyone working from the same version of the data. And for most teams, that shift has made discovery feel more manageable and far less fragile.
Manual Workarounds and Legacy Tools
Even now, some discovery work still relies on manual workarounds and legacy tools, usually layered on top of newer systems.
These approaches often develop over time as teams try to keep moving without fully rethinking their setup. But while they may feel familiar, they tend to add friction and risk when assembling evidence or trying to stay aligned with legal standards.
Common examples include:
- Tracking discovery status in spreadsheets shared by email
- Manually renaming and organizing electronic files in folders
- Printing electronic data to review alongside paper documents
- Copying text between documents to build responses
- Relying on local drives or outdated servers for storage
These methods can work in small bursts, but they don’t scale well. As data grows and deadlines tighten, the lack of integrated technological solutions becomes more noticeable.
Client and Court Expectations
Clients want to feel confident that relevant data is handled carefully and that costs stay predictable. They often ask practical questions. How much data needs review? How long will it take to collect data? Why does one phase of the review process cost more than another?
Meanwhile, courts bring a different kind of pressure. Deadlines are firm, production formats matter, and decisions around scope or privilege may need to be explained later.
In addition, judges expect teams to understand their own process and show that reasonable steps were taken to narrow data and produce documents correctly.
For example, a client may get frustrated if the review drags on longer than expected, while a court may question why certain materials were included or excluded. Those expectations push legal teams to stay organized, deliberate, and ready to explain their choices at every stage.
Time and Budget Constraints
Time and budget constraints sit at the center of almost every discovery decision. When review takes longer than expected, or costs climb without warning, pressure builds quickly from both clients and the court.
That’s why many firms spend time evaluating their eDiscovery platform early. The right software can reduce manual work, help teams move through review faster, and keep eDiscovery costs more predictable.
Some firms rely on free trials to test how a tool handles real data before committing, especially when budgets are tight and mistakes are expensive.
Without the right software in place, teams often compensate with extra hours or rushed decisions. As time goes on, that approach becomes harder to sustain. Investing in tools that match workload and timelines can make discovery feel less reactive and far more controlled.
How eDiscovery Fits Into a Litigation Strategy
Discovery often influences a case earlier than people expect. The choices made during eDiscovery can affect leverage, timing, and how arguments take shape, especially in these areas:
Early Case Insights and Leverage
Early discovery work can quietly change how a case feels from the inside. Once you start reviewing documents with a clear purpose, things tend to click faster. You see how events actually unfolded, who was involved, and where the story holds together or falls apart.
For example, a small batch of emails might confirm a timeline everyone assumed was shaky, or expose decision-making that the other side would rather not explain.
Early review can also surface potentially privileged documents or show that a large portion of the data is irrelevant or redundant information that doesn’t deserve more time.
Those insights shape real conversations. Some clients simply refuse to keep pushing once the risks are obvious. Others gain confidence when the evidence lines up in their favor.
Early clarity helps teams:
- Focus on the right custodians early
- Cut back on unnecessary reviews
- Spot weak spots before positions lock in
- Shape negotiation strategy sooner
Discovery’s Role in Motion Practice
Motion practice refers to the written requests lawyers file with the court asking for a ruling. These filings often deal with discovery disputes, procedural issues, or efforts to narrow the case, and they usually come with tight deadlines.
Discovery feeds directly into that work. When discovery is handled manually, pulling support for a motion can feel scattered.
Teams end up hunting for documents, double-checking versions, and stitching together citations while the clock keeps ticking. The pressure can make the process feel rushed rather than deliberate.
With eDiscovery, the transition feels smoother. Documents have already been reviewed, organized, and tied to specific issues, so the focus stays on the argument itself.
When a motion needs to be filed, you’re working from a record you already understand. That familiarity helps arguments land more cleanly and keeps motion practice grounded in the facts.
Using Discovery to Shape Settlement Strategy
eDiscovery often influences settlement discussions earlier than expected. Once documents are reviewed and organized, the case becomes clearer. The evidence starts telling a story, and that story matters when deciding how far to push or when to open negotiations.
For example, early document review might uncover emails that undercut a key argument or expose gaps in the other side’s claims.
In other situations, the record may strongly support your client’s position, which changes how firmly you hold your ground. eDiscovery tools make these signals easier to spot because documents are searchable, grouped, and tied to specific issues.
That visibility changes the tone of settlement talks. Parties adjust their expectations once the evidence is hard to ignore. Negotiations become more concrete, focused on what the documents show rather than assumptions or pressure tactics.
With a clearer record in hand, teams can make settlement decisions with more confidence and fewer unknowns.
Common eDiscovery Tools for Law Firms
Most law firms don’t rely on one tool to handle electronic discovery. Discovery work touches a lot of moving parts, so firms usually combine several tools depending on the case, the data involved, and how the team prefers to work.
Here are the types of tools law firms commonly use:
- Case assessment tools: Give you an early look at data volume and timelines, which helps shape case strategy before discovery requests expand.
- Data collection tools: Gather files from email, document storage, and other systems while keeping file details intact.
- Processing and review platforms: Prepare documents for review and apply smart filtering so teams are not wading through unnecessary material.
- Search and analytics tools: Use search filters and data analytics to surface patterns and narrow large data sets more quickly.
- Redaction and privacy tools: Handle data redaction to protect personally identifiable information and other sensitive content.
- Production and access tools: Support document delivery, permissions, and data security, often within cloud-based eDiscovery software.
The right eDiscovery technology depends on how your firm handles discovery day to day and how much control you want at each stage.
How Briefpoint Makes eDiscovery Work Without the Drag
eDiscovery has a way of taking over a case if you let it. Files can pile up, timelines can stretch, and hours can disappear into work that feels necessary but never strategic.
Most legal practice teams feel that tension, particularly as digital discovery keeps expanding.

Briefpoint is an AI-powered tool that steps in as a practical answer to that problem. It focuses on written discovery, where a lot of time quietly gets burned.
Meanwhile, Autodoc turns production files into Word-ready discovery responses with Bates citations in minutes.
Many firms see 30+ hours saved per case, which creates real cost savings without asking attorneys to give up control or change how they review work.
Is discovery taking more time than it should? Book a demo with Briefpoint today!
FAQs About eDiscovery for Law Firms
Do law firms still handle eDiscovery manually?
Some firms still handle parts of eDiscovery manually, especially on smaller matters, but eDiscovery often relies on manual techniques that slow things down and increase risk. As data volumes grow, most teams move toward discovery software to reduce repetitive work and keep reviews organized.
How do law firms keep track of what was reviewed and produced?
Modern eDiscovery tools rely on audit trails to show what happened at every stage, from collection to production. That visibility helps legal teams explain decisions, track changes, and respond confidently if questions come up later.
Is eDiscovery only practical for large law firms?
No. Large law firms often have more internal resources, but small law firms also benefit from the right eDiscovery software, especially tools with a clean user interface and simple user management that don’t require heavy setup.
What kinds of documents can eDiscovery tools handle?
Most platforms support multiple formats, help with limiting documents to what matters, and flag near duplicate documents so review stays focused rather than repetitive.
How does eDiscovery help protect sensitive information during discovery?
eDiscovery tools support secure document management by controlling who can access specific files and tracking how documents are reviewed and produced. Permissions, audit trails, and redaction tools help limit exposure of private and confidential information, which reduces the risk of accidental disclosure while still allowing teams to move discovery forward efficiently.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
How to Automate Legal Workflows One Process at a Time
How to Automate Legal Workflows One Process at a Time
If you paused your day and listed out everything that happens around your legal work, not the analysis, but the copying, tracking, formatting, and follow-ups, the list would get long fast. Most of that work follows the same path every time, yet it usually still eats up hours.
That’s the gap legal workflow tools are designed to close. They don’t change how you practice law. Instead, they change how work moves around it. Intake flows into drafting, drafting flows into review, and deadlines stop living in five different places.
This guide breaks down how legal workflow automation actually works in practice. You’ll see which tasks are easiest to automate, how legal workflow tools fit together, and why discovery drafting is often the cleanest place to start when you want results without disruption.
What Is Legal Workflow Automation?
Legal workflow automation is a broad concept, and it can mean different things depending on who you ask.
For some teams, it focuses on document creation. For others, it shows up in task routing, approvals, or deadline tracking. The common thread is using legal technology to handle work that follows a predictable pattern.
At a basic level, legal workflow automation uses automated workflows to handle work that follows the same pattern over and over.
Repetitive tasks like drafting standard documents, moving discovery requests through review, assigning internal follow-ups, or pulling matter details stop requiring the same manual steps each time.
For law firms and in-house teams, this changes how legal operations run day to day. Legal professionals still review the work and make judgment calls, but they spend less time on menial tasks like moving files, copying language, or tracking status updates.
Legal workflow automation is not tied to one tool or feature. It’s a practical way to organize legal work so the predictable parts move faster, while people stay focused on the decisions that actually need legal experience.
Legal Tasks That Are Best to Automate First
If you’re getting started with legal workflow automation, the smartest move is to focus on work that already follows a clear pattern. These are the tasks that show up often, take time, and rarely need to be reinvented:
Discovery Drafting and Response Preparation
Discovery drafting is often the first place legal teams feel the drag of manual processes. Requests come in, documents pile up, and hours disappear into copying language, tracking citations, and double-checking references. The work is familiar, but the effort adds up fast.
This is why discovery drafting tends to be the first win for document automation. The structure rarely changes. What changes are the facts, the productions, and the references tied to each request.
Automation handles those routine tasks so you are not rebuilding the same response from scratch every time.
Tools like Briefpoint are designed specifically for this stage of litigation. Briefpoint uses your productions and case materials to generate documents that are already mapped to discovery requests, complete with citations and formatting aligned to how discovery actually gets served.
Common discovery tasks that benefit from automation include:
- Drafting responses to interrogatories, requests for production, and requests for admission
- Pulling facts and references directly from productions
- Applying consistent language to objections and responses
- Reducing repetitive manual edits across documents
When discovery drafting moves faster, everything downstream feels lighter. To see how this works in practice, learn more about Briefpoint and how it supports automated discovery workflows.
Intake Forms and Matter Setup
Intake and matter setup often feel routine, but they shape how smoothly everything runs later.
Details come in through emails, calls, or shared docs, then someone has to gather it all, enter it again, and make sure nothing was missed. That back-and-forth adds friction before the real legal work even starts.
Legal automation turns intake into a clean starting point. A legal intake form collects the right information upfront and feeds it directly into your systems. Client intake data, matter details, and key dates land where they belong without extra handling.
In turn, legal departments get a clearer picture of the work ahead from the start, and fewer follow-ups slow things down.
Picture a new matter opening with all the basics already filled in, tasks assigned automatically, and the right people looped in right away. That same flow works for contract reviews, investigations, or ongoing advisory work. The process stays consistent, even as the work itself changes.
Standard Legal Document Drafting
Thanks to modern legal tech, you don’t need to reinvent routine documents. Most standard drafts rely on the same clauses, the same structure, and the same information, and automation can take care of those repetitive details.
Artificial intelligence can handle document handling without turning your work into a black box. You enter the details once, the system generates the draft, and you step in to review and adjust.
So, the focus shifts away from tedious tasks and back to legal judgment, which is where your time actually matters.
Documents that are commonly automated include:
- Engagement letters
- NDAs
- Fee agreements
- Settlement agreements
- Employment agreements
- Demand letters
- Basic contracts and amendments
Automating this kind of administrative work helps cut repetition, reduce rework, and enhance productivity without changing how you prefer to work.
Internal Reviews and Approvals
Automated review and approval workflows route documents through the right reviewers in a defined order, with each step tracked automatically. Once a document enters review, the system controls who sees it next and what needs to happen before it moves forward.
Legal tech keeps comments, approvals, and versions connected to the same document, so reviewers always work from the current draft.
Manual review still happens, but the surrounding coordination runs quietly in the background. Plus, review status stays visible without extra messages or check-ins.
A contract update, for example, can move from legal review to compliance sign-off and then to final approval without anyone managing the handoffs. The workflow holds the sequence together while reviewers focus on substance rather than logistics.
Deadline Tracking and Reminders
Automated deadline tracking keeps dates tied to the work itself and not scattered across calendars or notes. Tasks, filings, and reviews carry their own due dates, and those dates move as the workflow progresses.
For one, reminders can trigger based on the schedule you set, which helps keep things on track without constant manual check-ins.
This approach works well when multiple workflows run at the same time and timelines overlap. You can see what’s coming up, what’s approaching fast, and how tasks line up without piecing it together yourself.
With task management built into the workflow, deadlines stay visible and connected from start to finish. In turn, this reduces the chances of missed deadlines while keeping the day organized.
Status Updates and Task Assignments
Status updates and task assignments can update automatically as work moves through a workflow. Progress reflects what has already happened, without requiring separate tracking or manual updates.
This keeps legal processes easier to follow when work overlaps or changes direction. Information stays current as matters develop, which reduces the need for administrative tasks tied to monitoring and reporting.
In other words, workflow efficiency improves simply because the system reflects the work as it unfolds.
Types of Legal Workflow Automation Tools
There isn’t really a single product called a “legal workflow automation tool.” In practice, legal workflows get automated through a mix of tools that handle different parts of the work. Each one covers a piece of the process, and together they shape how work moves through a legal team.
Here are the main categories you’ll see most often:
- Legal practice management software: Handles matter tracking, task management, deadlines, and high-level organization for day-to-day legal work.
- Document generation tools: Support document automation by turning structured inputs into drafts, which reduces manual legal drafting and repetitive edits.
- Case management systems: Keep matter information, timelines, communications, and filings connected in one place throughout a case.
- Document management platforms: Store, organize, and version legal documents so files stay searchable and current as work evolves.
- Document review tools: Assist with reviewing large volumes of documents, flagging patterns, and managing review workflows.
- Legal research tools: Help legal professionals find relevant authority and reference materials more efficiently during active matters.
- Legal workflow automation software: Connects tasks, documents, and reviews into structured workflows that move work forward automatically.
How to Automate Legal Workflows
Now that you’ve seen which legal tasks tend to automate well, the next move is turning one of those tasks into a workflow your team can actually use.
Keep it simple at first, then build from there as the process starts to feel familiar:
Step 1: Pick One Workflow With Clear Steps
Pick something you already know well. If you can explain the steps without thinking too hard, that’s a good place to start. Early legal process automation works best when the process feels familiar.
Discovery response drafting is a solid example. Requests arrive, productions get reviewed, responses take shape, citations get added, and the draft goes through review before it’s served.
The details change, but the flow stays the same.
Step 2: Write Down the Exact Inputs You Need
Before automating anything, get specific about the information the workflow depends on. Walk through the entire process and note what needs to be available at each stage. This keeps the setup practical and avoids gaps later.
Typical inputs include:
- Client or matter details
- Key dates and deadlines
- Document or request types
- Source files or productions
- Review or routing preferences
Remember: Clear inputs matter even more when workflows support broader strategic initiatives.
Step 3: Standardize Templates and Rules
Automation relies on consistency. Templates and rules define how documents look, how decisions get made, and how work moves from one step to the next.
This often includes:
- Document templates and formatting
- Standard response language
- Review and approval sequences
- File naming and organization rules
Step 4: Choose the Tools That Fit Your Process
Now it comes down to picking tools that actually make sense for how you work. You’re not looking for the most impressive feature list. You’re looking for something that fits into your day without getting in the way.
The right tools take care of time-consuming tasks that quietly eat up countless hours, while everything else stays familiar. If a tool feels like it’s fighting your process, it probably will. When it fits naturally, you notice it less, and that’s usually a good sign for long-term use and optimal performance.
Step 5: Build the Workflow and Test It on Real Matters
Once the pieces are in place, it’s time to build the workflow and see how it holds up in real work.
Start with existing workflows rather than hypothetical ones. Real matters reveal gaps and edge cases much faster than test data ever will.
As you test, keep the focus on how the workflow supports the people using it. Team members should understand what the workflow does, what it does not do, and where they step in.
Keep in mind that proper training matters here, even if the workflow feels simple on paper.
Testing usually includes:
- Running the workflow on a small number of live matters
- Watching where manual steps still show up
- Adjusting rules, templates, or inputs as needed
- Gathering feedback from each team member involved
The goal is not perfection. A workable setup can significantly reduce repetitive work, enhance efficiency, and leave more room for strategic work as the workflow settles into daily use.
Step 6: Add Review Checks and Approval Points
Automation still needs human eyes at the right moments. Review checks and approval points give you natural pause spots before work moves forward, especially when client information or sensitive details are involved.
A discovery response, for example, might be drafted automatically, but wait for attorney review before it’s finalized.
A contract can move through its workflow but stop for approval before it goes out the door. Those moments matter, and building them in helps with error reduction without breaking the flow.
Most teams rely on existing systems for these checks, which keeps the process familiar. Reviews happen in the same way each time, ensuring consistency while leaving room for judgment when it counts.
Step 7: Connect Systems and Reduce Double Entry
You shouldn’t have to enter the same information three different times just to keep work moving. When systems are connected, details flow naturally from one step to the next, and seamless integration starts to feel like common sense.
Information from intake can carry through to matter records, documents, and follow-on tasks without being retyped. That helps drive efficiency and reduces human error when things change.
It also makes it easier to ensure compliance, since the same data stays consistent everywhere it’s used.
Step 8: Roll It Out, Track Results, and Refine
Once the workflow is working, it’s time to roll it out more broadly and see how it performs in day-to-day use. Start with one practice area or team before expanding further, especially if the workflow touches multiple roles.
As it runs, pay attention to how it’s actually used:
- Where people pause or work around the workflow
- Which steps save time and which still feel manual
- How the workflow fits into existing routines
- Feedback from team members using it daily
For law firms and corporate legal departments, this stage helps surface real impact. Over time, small adjustments can improve fit, reduce friction, and bring down operational costs without reworking the entire process.
Why Discovery Drafting Is the Smartest Place to Start
Legal workflow automation works best when it starts with work that already follows a clear pattern.
Discovery drafting fits that description better than almost anything else. The steps are predictable, the volume is high, and the time cost is hard to ignore. So, automating that part of the workflow creates immediate relief without changing how you practice law.

Discovery responses don’t need reinvention. They need speed, consistency, and accuracy. When drafting, citations, and formatting stop consuming hours, the rest of the workflow opens up naturally.
From there, it becomes easier to automate intake, reviews, deadlines, and handoffs using the same approach.
Briefpoint was built with this exact starting point in mind. It focuses on discovery drafting first, giving legal teams a practical way to begin automation without overhauling everything at once.
FAQs About How to Automate Legal Workflows
What are the benefits of legal workflow automation?
The main benefits of legal workflow automation show up in day-to-day work. Processes take less time, handoffs feel clearer, and repetitive steps fade into the background. Automation also supports minimizing errors because the same rules and inputs apply every time work moves forward.
How does automation affect client communication?
Automation helps keep client communication more consistent. Updates happen closer to real time, information stays accurate, and fewer details get lost as matters progress. That steady flow tends to improve client satisfaction without adding extra steps for the legal team.
Can a small firm automate legal workflows effectively?
Yes. A small firm often benefits quickly because workflows are easier to define and change. Automating intake for a new client, discovery drafting, or internal reviews can make a noticeable difference without a large rollout.
How does legal workflow automation help business stakeholders?
Automation gives business stakeholders clearer visibility into timelines, progress, and expectations. In the legal industry, that clarity helps align legal work with broader business needs while keeping teams focused on the work itself.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
An Overview of the Typical eDiscovery Workflow
An Overview of the Typical eDiscovery Workflow
The eDiscovery workflow brings structure to work that already carries enough complexity on its own.
Rather than treating discovery as a series of disconnected tasks, it shows how digital information moves through a case, from early planning through production and closeout.
But, of course, no two teams run discovery the exact same way. Tools, case types, and internal preferences all shape how the work gets done, especially as cloud-based eDiscovery platforms continue to change how teams collect, review, and share information.
Even so, the overall flow stays fairly consistent. Knowing that flow helps you anticipate what’s coming, make cleaner decisions at each stage, and keep discovery moving.
In this guide, we walk through each stage of a typical eDiscovery workflow and explain what happens at every step.
What Is eDiscovery?
The eDiscovery process (electronic discovery) is how legal teams handle electronically stored information (ESI) during litigation and investigations.
Emails, documents, chat messages, cloud files, and mobile data all come into play. If it lives on a screen, it’s likely part of the discovery process.
Not that long ago, discovery looked very different. Paper files, boxes of documents, and manual review did most of the heavy lifting. That approach could work when data was limited and mostly physical.
Today, information spreads across inboxes, apps, shared drives, and systems that change constantly. Manual discovery struggles to keep up.
eDiscovery evolved to match that reality. With eDiscovery software, teams can collect and review digital information in a more structured way. Search tools, filters, and review workflows help narrow large data sets down to what actually matters.
In short, eDiscovery brings clarity to digital evidence. It enables legal teams to manage volume, move faster through review, and stay organized as cases progress, without relying on outdated, labor-heavy methods.
What Does a Standard eDiscovery Workflow Look Like?
Every law firm and legal team has its own way of handling discovery. Workflows shift based on case size, deadlines, risk tolerance, and the tools in use. Some teams lean heavily on modern platforms, while others rely on a mix of software and manual steps.
Even with those differences, most matters follow a familiar path. The steps may overlap or move faster depending on the setup, but the overall flow tends to stay consistent. Here’s how eDiscovery usually unfolds in practice.
Case Assessment and Planning
This is the point where discovery starts to take shape. Before data gets collected or reviewed, you need a clear sense of what the case calls for and what can wait. Early decisions here tend to influence everything that follows.
Early case assessment helps narrow the focus before effort and cost ramp up. You’ll usually see teams focus on things like:
- Identifying the claims, defenses, and key issues
- Flagging custodians tied to potentially relevant data
- Spotting systems that may hold relevant documents
- Estimating data volume and review effort
- Setting timelines and internal responsibilities
This stage also sets expectations. What qualifies as relevant information? What falls outside the scope? Always remember that getting alignment early reduces back-and-forth later in the eDiscovery workflow.
Data Identification
This step is about getting clear on where information actually lives. In most cases, relevant material sits in more places than people expect, especially with how work happens today.
You’re looking for electronic data that could matter to the case, not trying to grab everything at once. That means tracking down potentially relevant ESI, understanding who controls it, and noting how it’s stored. You also need to know if there are any ESI protocols in place.
Data identification often includes a mix of familiar and less obvious data types, such as:
- Email and calendar systems
- Documents and spreadsheets
- Chat and collaboration tools
- Cloud storage and shared drives
- Social media posts
- Mobile data and text messages
- Video files, images, and audio
- Internal systems and databases
Spending time here helps surface critical documents and key evidence early. It also reduces surprises once collection starts and gives the discovery process a stronger foundation.
Data Preservation and Legal Holds
Preservation and legal holds are basically the moment you hit pause on everyday data habits. Once a legal matter is reasonably on the horizon, certain information can’t keep cycling through normal deletion rules.
A legal hold lets people know they need to retain electronically stored information tied to the case. Say an employee’s inbox clears messages after a set period.
If that person becomes a custodian, those emails need to stay put. The same goes for shared folders, chat platforms, and other places where sensitive data may live.
This step also requires care around data protection regulations and regulatory compliance. Preserving information doesn’t mean opening access to everything. Teams still have to handle personal and confidential material thoughtfully.
Handled early, preservation keeps the discovery process on solid ground. It helps avoid awkward questions later about missing data and shows that the team took its obligations seriously from the start.
Data Collection
Data collection is where information moves out of its original home and into a review-ready environment. The focus stays on accuracy and consistency, especially once deadlines and pressure start building.
At this stage, teams aim to manage data carefully without pulling far more than the case requires. The sheer volume of digital information makes that balance important.
You’ll usually see collections handled with goals like these:
- Gathering data from identified sources: Pulling emails, files, and messages tied to custodians and systems flagged earlier.
- Maintaining defensibility: Tracking where data came from and how it was handled throughout the process.
- Limiting over-collection: Avoiding unnecessary copies of multiple documents that don’t add value.
- Reducing disruption: Collecting information without interfering with day-to-day business activity.
Strong data management matters here. The right eDiscovery software can help manage data volumes, keep collections organized, and reduce manual effort before review even begins.
Processing
Processing is the cleanup phase that turns raw data into something you can actually work with. Collected files often come in different formats, versions, and structures, which makes direct review impractical without some prep.
This step helps organize unstructured data while keeping legal requirements in mind. It’s also where eDiscovery tools start doing a lot of behind-the-scenes work.
Processing typically includes tasks like:
- Converting files for review: Turning emails, documents, and media into formats that review platforms can handle.
- Removing duplicates and system files: Cutting down noise so reviewers spend time on meaningful content.
- Extracting text and metadata: Making information searchable and easier to sort.
- Applying basic filters: Narrowing data sets using dates, custodians, or keywords.
Good processing sets the tone for review. Clean, organized data saves time, controls cost, and keeps the workflow moving without unnecessary friction.
Review and Analysis
This is where eDiscovery starts to feel real. Documents get opened, read, and evaluated to see how they fit into the case.
Relevance, responsiveness, and privilege all come into focus here, and decisions made at this stage often shape what gets produced later.
In the past, reviewing meant reading everything from top to bottom. That approach breaks down fast once data volumes grow.
Today, analysis tools use artificial intelligence and natural language processing to surface patterns, cluster related documents, and flag items likely to matter. Plus, advanced analytics help reviewers spend time where it counts.
For example, if a case centers on a contract dispute, analytics can help group communications tied to negotiations, amendments, or approvals, even if the language varies. Reviewers can then focus on those threads without combing through every unrelated email.
Even with smarter tools, human judgment remains essential. Context, nuance, and legal significance still require careful review. Technology-assisted review helps narrow the field, but people make the final calls that move the discovery process forward.
Privilege Review and Redactions
Privilege review is the step where teams slow things down and double-check what should stay private. The goal is to prevent protected communications from ending up in front of opposing counsel during legal proceedings.
This usually involves attorney-client communications, legal advice, and internal analysis. Sometimes it’s straightforward. Other times, the same document mixes privileged content with information that needs to be produced.
That’s where redactions come in. They allow part of a document to move forward while keeping sensitive sections hidden.
This stage matters for more than caution alone. Regulatory requirements and court expectations leave little room for error, and accidental disclosure can create real potential risks. Once something is produced, pulling it back can be difficult.
Privilege review helps teams effectively manage exposure while keeping the eDiscovery process on track. It’s often the last meaningful checkpoint before documents leave your control, which makes accuracy and consistency especially important here.
Production
Production is when reviewed documents officially leave your hands and go to the other side. In civil litigation, this step carries real consequences, since errors can lead to disputes, delays, or court involvement.
The focus here is precision. Only specific documents approved during the review process should move forward, and they need to follow the agreed production rules. Formatting, labeling, and confidentiality designations all matter.
Production typically involves:
- Selecting final responsive documents
- Applying Bates numbers and confidentiality markings
- Confirming redactions display correctly
- Packaging files in the required format
Modern eDiscovery platforms help legal professionals handle this work without manual file handling. That structure allows legal teams to stay consistent, even when production includes thousands of records.
For example, a large email production may require keeping message threads and attachments grouped together. With the right legal workflow tools, those relationships stay intact automatically, which reduces mistakes and follow-up issues.
Once produced, documents are delivered to opposing counsel, and discovery often continues with additional requests or clarifications.
Delivery and Service
Delivery and service are the handoff points. After final production is ready, documents are formally shared with the other side in line with legal obligations and any agreed procedures. This step may sound simple, but it still deserves attention.
Today, many corporate legal teams rely on collaboration platforms or cloud-based eDiscovery platforms to handle delivery. These tools make it easier to transfer large files securely, track access, and confirm receipt without relying on physical media or unsecured file sharing.
Service also creates a clear record. Who received the production, when it was delivered, and what was included all matter if questions come up later. Even small issues, like a missing file or a corrupted attachment, can slow things down if they aren’t caught early.
Once delivery is complete, discovery rarely pauses for long. Follow-up requests, questions, or supplemental productions often come next, which makes clean service an important checkpoint before moving forward.
Post-Production and Matter Closeout
Once documents are out the door, discovery doesn’t automatically shut down. There’s usually a stretch where teams stay engaged, watching for follow-up requests and making sure nothing gets overlooked as the case moves forward.
This phase often includes work like:
- Handling additional discovery responses: Responding to questions or producing supplemental material tied to earlier document review.
- Keeping tabs on obligations: Monitoring legal holds and knowing when they can safely be lifted.
- Staying organized: Using centralized tracking to track progress and keep timelines visible.
- Wrapping up data management: Archiving files or clearing retained data at the right point in the eDiscovery lifecycle.
- Looking back: Reviewing how the process played out and noting improvements for future matters.
An eDiscovery solution can help bring closure to this stage, keep records clear, and make sure decisions are documented.
Clean closeout reduces risk, supports future reference, and gives teams a clearer exit once discovery truly ends.
Bringing eDiscovery Back to a Manageable Process With Briefpoint
eDiscovery works best when each stage stays focused and predictable. The challenges usually show up during response drafting, objections, and production prep, where manual work can slow everything down.

Briefpoint is the AI tool that focuses on those pressure points.
Along with tools that support faster, more consistent discovery responses, Autodoc helps turn productions and case files into ready-to-serve responses with citations already in place. That means less time copying, pasting, and cross-checking documents.
Resources like the Discovery Objections Cheat Sheet also give teams a practical reference when decisions need to be made quickly, without overthinking each response.
If discovery work feels heavier than it should, seeing how Briefpoint handles these steps can be eye-opening.
FAQs About eDiscovery Workflow
What is an eDiscovery workflow?
An eDiscovery workflow is the sequence that legal teams follow to handle digital information during a matter. It covers everything from identifying data sources to reviewing documents and producing them. The goal is to keep information organized, defensible, and easy to manage while protecting sensitive information along the way.
What are the steps in the eDiscovery process?
Most workflows move through planning, data identification, preservation, collection, processing, review, production, and closeout. Some teams compress or combine steps depending on the case and their existing systems, but the overall structure stays familiar.
How does eDiscovery work?
eDiscovery works by collecting electronic data, preparing it for review, and narrowing it down during the review phase. Technology helps reduce human error, manage large volumes, and surface relevant material faster, which supports trial preparation without overwhelming the team.
What is an example of a workflow?
In a commercial dispute, emails and documents may be collected, processed, reviewed with predictive analytics, produced to the other side, and then revisited if follow-up requests arise. Each step builds on the last, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs over time.
What is cross-border eDiscovery?
Cross-border eDiscovery involves data stored in multiple countries. It often raises concerns tied to data breaches, privacy laws, infrastructure costs, and eDiscovery costs, since rules and handling requirements can vary significantly by location.
A Comprehensive Guide to Legal Document Automation
A Comprehensive Guide to Legal Document Automation
Legal document automation usually gets talked about in big, abstract terms. In reality, it shows up in very specific moments, drafting the same document again, fixing the same details, and spending time on setup work that never really changes.
Legal document automation software is designed to take that repetitive work off your plate.
It turns familiar drafting patterns into structured workflows, so documents come together faster and with fewer manual steps. You still review and revise, but you’re not rebuilding the foundation every time.
This guide focuses on how legal document automation works in practice. It covers how documents are created, where automation helps most, and what to pay attention to when evaluating tools.
What Is Legal Document Automation?
Legal document automation refers to using software to create legal documents with far less manual drafting.
You usually answer a set of questions, pull in existing matter or client data, and the document builds itself based on rules you’ve already defined. That means no starting from scratch or copying language from old files and hoping it still applies.
For legal professionals, this usually shows up in routine work. Engagement letters, discovery responses, court filings, and contracts all follow familiar patterns. Legal document automation software takes those patterns and applies them consistently.
This means that names, dates, clauses, and references fill in automatically, while the structure stays aligned with how you already work.
Still, automated legal documents require review. The difference is how you get there. Legal document creation moves faster because the base draft is already complete and organized, which leaves more time for judgment calls and less time on mechanical edits.
Legal Document Automation vs. Traditional Drafting
Traditional legal drafting usually means starting with a prior document and working forward from there. You copy language, update the facts, adjust clauses, and read through everything to confirm it still fits the situation.
That approach has worked for a long time, but it relies on manual processes at every step. When documents go through multiple revisions, small details can be overlooked, and older language can carry over without anyone noticing right away.
On the other hand, legal document automation works differently. Document templates are set up in advance, with rules that control how the language changes. When you create automated legal documents, the software pulls in client or matter information and builds the draft for you.
For instance, a discovery response can reflect the case type. A contract can apply the right terms based on jurisdiction or deal structure. The framework stays consistent, and the details adjust as needed.
At the end of the day, automation tools don’t replace review or decision-making. They reduce the time spent assembling documents so the focus stays on substance, accuracy, and legal judgment rather than repetitive drafting work.
How Legal Document Automation Works
The process behind legal document automation is fairly simple: the software manages the routine steps, and legal teams keep control over wording and review.
Here’s how it usually comes together.
Document Templates
Document templates are the foundation of legal document automation. You set them up once inside legal document software and reuse them every time you need to create documents with the same structure. The language stays consistent, while the details change based on the matter.
This cuts down on manual data entry and leads to fewer mistakes during drafting. One template can also support multiple documents, which helps when the format stays the same but the facts vary. You still control the wording, but the software handles the repeatable setup.
Templates are commonly used for:
- Contracts and agreements
- Discovery responses
- Court filings
- Client letters
- Internal legal forms
Rules and Logic
Rules and logic control how a document changes as information is added. This is the part that allows document assembly software to handle complex legal documents without locking you into a single version of the text.
Conditional logic sits behind the scenes and decides which sections appear, which clauses change, and which language gets left out.
For example, a document can include different legal language based on jurisdiction, party type, or claim category.
A discovery response might apply one set of discovery objections for a product case and a different set for an employment matter. Or a contract might adjust indemnity or termination terms based on deal size.
You don’t rewrite the document each time. The rules handle those variations automatically, and the structure stays intact. That keeps the draft consistent while still allowing it to reflect the facts of the matter.
Data Collection and Intake
Data collection and intake are simply how information gets into the document.
In a law firm document automation setup, this step replaces back-and-forth emails, notes in different places, and last-minute clarifications. You gather the key details once, and everything downstream works from that same source.
Most teams use client intake forms or short internal questionnaires. The questions are practical and tied directly to the document, so you’re not collecting information “just in case.”
Details like names, parties, dates, claims, and jurisdiction flow into the document workflow automatically, which cuts down on retyping and cleanup later.
This also helps earlier in the process. If something is missing or doesn’t make sense, you see it right away, before a draft ever goes out for review.
Common ways teams collect information include:
- Client intake forms that capture basic party and matter details up front
- Internal questionnaires filled out during case setup or review
- Matter or case systems that already store ongoing information
- Uploaded files used as reference points during drafting
During this step, the central goal is to start with cleaner inputs so the document comes together with fewer fixes later.
Automated Document Assembly
Automated document assembly is simply the point where the draft gets built for you. Once the information is collected and the rules are applied, legal automation software uses automated templates to generate documents as a complete first draft, without anyone piecing it together manually.
Take an RFP response as an example. Party details come from intake, objections adjust based on the matter, and citations fall into place automatically.
For a contract, the right clauses appear based on jurisdiction or deal terms, and the draft is ready to review. The document drafting process still includes edits and judgment. However, the setup work is already handled.
This is where legal tech and automation workflows make the biggest difference. You move straight into reviewing the document, not building it from the ground up.
For litigation teams, tools like Briefpoint apply this approach directly to high-volume document work, helping generate documents faster while keeping review and control firmly in your hands. See how it works.
Review and Final Edits
Review and final edits are still a critical part of the process, especially when dealing with complex documents. Automation handles the setup, but the responsibility for accuracy and judgment stays with the person reviewing the draft. This is where legal experience matters most.
Because the document is already structured and populated, review time is usually spent on substance rather than cleanup.
You’re checking arguments, legal language, and context, not fixing formatting or retyping basic details. That shift helps reduce human error, particularly the small mistakes that tend to appear during manual edits.
The end result is professional documents that reflect the facts of the matter and the reviewer’s judgment.
Types of Legal Documents You Can Automate
Legal document automation is a good fit for documents that follow a familiar pattern but change depending on the matter.
If your team relies on reusable templates or regularly updates older files, automation can support drafting documents without forcing everything into a one-size format.
Common document types include:
- Legal agreements: Contracts, NDAs, and other legal agreements that adjust terms based on parties, jurisdiction, or deal structure while keeping language consistent.
- Court documents: Pleadings, motions, and discovery responses that pull in case details and apply the correct formatting and legal language.
- Internal legal documents: Forms, approvals, and policy documents used by in-house legal departments to keep work organized and consistent.
- Customized legal documents: Documents built from a shared structure that change based on inputs like claim type, matter status, or jurisdiction.
- Legacy documents: Older templates and files that can be converted into automated formats, making them easier to update and reuse.
These documents all benefit from legal automation when the structure stays stable, but the facts change from one matter to the next.
What Are the Benefits of Legal Document Automation?
Legal document automation affects daily drafting work more than anything else. Once the repetitive steps are taken out of the process, these benefits tend to show up pretty quickly:
Improved Drafting Speed
Better drafting speed is probably the easiest benefit to spot, and we’ve touched on it already throughout this guide. At this point, it should feel fairly obvious why it happens. When automation platforms handle the setup work, you’re no longer building documents piece by piece.
As soon as you create automated templates, the starting draft is already there. Information fills in, sections adjust automatically, and the document is ready for review much earlier in the process.
In turn, less time goes into assembly, which means drafts move forward faster without rushing the review.
Greater Consistency in Legal Language
This benefit comes from taking the drafting decisions out of the moment and locking them into the document generation process. When the same templates and rules are used every time, the language stays aligned from one document to the next.
For example, a firm might use one approved set of definitions or standard clauses for a specific type of matter. With document automation in place, those sections appear the same way every time, rather than being copied from different versions of old files.
That helps keep compliant documents aligned with internal standards and current requirements, but without relying on memory or last-minute checks.
Reduced Manual Data Entry
Reducing manual data entry happens by removing steps that don’t add value. When a template exists, and workflow automation pulls in information automatically, the document no longer depends on repeated typing to come together.
Repetitive drafting tasks like inserting names, dates, and references happen once at the intake stage rather than throughout the document. On the flip side, automation keeps details aligned and reduces the amount of cleanup needed during review.
Lower Risk of Human Error
Lower risk of human error comes from taking routine edits out of the drafting stage. Automated document drafting handles the parts of the process that usually lead to small but costly mistakes, which helps keep accurate legal documents on track.
Common drafting errors include:
- Misspelled party names carried over from prior files
- Incorrect dates copied from older documents
- Inconsistently defined terms used throughout a draft
- Missing or duplicated sections after multiple revisions
When those details are handled automatically, review time can focus on substance rather than catching avoidable errors.
More Predictable Document Workflows
Ever had a drafting task feel unpredictable, even though the document itself was familiar? A missing detail or a late change can easily slow things down.
More predictable document workflows happen when you have a clear drafting path from start to finish. With document automation solutions in place, the steps stay consistent.
The right information gets collected early, drafts follow the same structure, and review happens at a known point in the process. This makes it easier to plan work, respond to legal issues as they arise, and keep documents moving.
What to Look for in Legal Document Automation Software
Choosing the right legal document automation software comes down to how well it fits into real legal work. The best legal document automation tools support how documents are already drafted, reviewed, and managed, rather than forcing teams to change everything at once.
Key things to look for include:
- Template flexibility: The software should support complex templates that reflect how your documents actually work, not just basic forms.
- Rules and logic support: Strong automation software for law allows conditional logic, so the language adjusts based on the matter details.
- Seamless integration with existing tools: Look for systems that work alongside existing tools like case management or legal document management platforms.
- Version control: Clear tracking of edits and updates helps teams avoid confusion, especially in large law firms.
- Collaboration and review controls: Drafts should move easily between contributors without losing structure or context.
- Support for different team types: The software should work equally well for large law firms and in-house legal teams.
- Document management compatibility: Generated files should fit cleanly into your document management system without extra cleanup.
Legal Document Automation That Fits How Litigation Actually Works
Legal document automation sounds broad until you see it applied to a specific problem. For litigation teams, that problem is discovery. Volume is high, deadlines are fixed, and the margin for error is small.
Briefpoint focuses on that reality rather than trying to cover every document under the sun.

Briefpoint supports the full discovery workflow, from propounding RFAs, RFPs, and interrogatories to responding with consistent objections, client-collected answers, and properly formatted outputs.
Autodoc is part of that system. It handles the most time-consuming step by turning productions and case files into Word-ready discovery responses with Bates citations and a service-ready production package.
Nothing about the process removes judgment or review. It shortens the path to a usable draft and keeps everything in a format attorneys already trust.
If discovery drafting keeps eating up hours that should go elsewhere, book a demo now.
FAQs About Legal Document Automation
What is legal document automation?
Legal document automation uses software to create documents based on structured templates and predefined rules. Information like case data or party details fills in automatically, so documents follow the same structure every time without manual rebuilding.
Is there an AI for legal documents?
Yes. Many tools use AI to support drafting, issue spotting, and document organization. In practice, AI usually works alongside templates and rules rather than replacing review. This can support improved client service by freeing up time for actual legal work.
Can ChatGPT write legal documents?
ChatGPT can draft general language, but it isn’t designed to generate service-ready legal documents tied to matter management, existing systems, or firm standards. It also doesn’t pull directly from case data or handle formatting and citations the way legal tools do.
What is the best document automation software?
The best option depends on how your team works. Software for law firms should fit into existing systems, support in-house teams as well as litigation workflows, and reduce drafting steps to just a few clicks without lowering client satisfaction.
What Is Legal Document Management?
What Is Legal Document Management?
At some point, every legal team has had the same moment. You open a document you worked on last week, only to realize there are three other versions with almost the same name.
One lives in a shared drive. Another came through email. A third is saved locally, and no one remembers which one went out.
That’s how outdated legal document management practices tend to show themselves. Perhaps not as a single failure, but as small, everyday frustrations that pile up.
Today, legal document management exists to bring order back to that process. It creates a clearer way to handle legal files as they move through drafting, review, and final use, to make sure that work stays focused on substance rather than on sorting out documents.
But what does that actually look like day to day?
In this guide, we’ll break down what legal document management is, how it works in practice, and why it’s so important.
Legal Document Management Explained
Legal document management comes down to control and clarity. You’re dealing with a steady flow of legal files, many of which change multiple times before they’re final. And without a clear system, it’s easy to lose track of what’s current, what’s been approved, and what still needs work.
A legal document management system gives those files a single home and a clear structure. Drafts, revisions, and final versions stay connected, so you’re not guessing which document to trust.
For legal professionals, that reliability matters. For example, when a deadline hits or a client asks for something specific, you can pull the right file quickly and move on.
Document workflows make the difference here. Files move through legal drafting, review, and approval in a predictable way. Comments stay tied to the document, changes are easy to follow, and everyone knows where things stand.
The result feels simple. At the very least, you’re experiencing less searching, fewer mistakes, and legal work that flows without unnecessary back-and-forth.
What Is Document Management Software?
Up to this point, legal document management has been about the practice itself: how legal files are organized and handled through real work. Document management software is the tool that supports the process day to day.
Legal document management solutions provide a structured place for documents to live while work is in motion. They make it easier to track each document version, share files without losing control, and keep a record of activity tied to regulatory compliance.
Typical features include:
- Document version tracking: Keeps changes and approvals connected to a single file so teams can review history, confirm updates, and avoid confusion during revisions.
- Access logs and audit trails: Records who accessed documents, what actions were taken, and when activity occurred, which supports internal oversight and compliance reviews.
- Document sharing: Allows files to be shared internally or externally with defined permissions, reducing reliance on email attachments and duplicate copies.
- Workflow automation: Supports review and approval flows by guiding documents through defined steps rather than informal handoffs.
- Automated templates: Help standardize commonly used documents and reduce repetitive drafting across similar matters.
Why Proper Legal Document Management Matters
Now that the basics are clear, the next step is understanding what legal document management actually delivers in practice. Let’s talk about the benefits and why they matter during daily legal work:
Reducing Errors and Rework
Most document mistakes don’t come from a lack of skill. They actually come from confusion.
Multiple drafts floating around, unclear handoffs, and no single source of truth all create room for human error. However, a consistent legal document management process can close those gaps and bring stability to the law firm’s workflow.
Many law firms spend more time fixing document issues than they realize. Version clarity, controlled access, and predictable document movement remove that backtracking. This way, you spend less time correcting avoidable problems and more time pushing work to completion.
Saving Time on Document Retrieval
Document retrieval shapes how smoothly legal work moves during the day. Time disappears when client documents live in multiple places or follow an inconsistent organization, because every search turns into a small decision-making exercise.
Good legal document storage reduces that mental load. Files follow a consistent structure, tagging files stays logical, and document access remains easy to understand. The essential features support quick retrieval without forcing you to stop and rethink how the system works.
Over time, this keeps your attention on the matter at hand rather than on locating documents or verifying details.
Supporting Compliance and Recordkeeping
Compliance and recordkeeping depend on consistency. Legal workflows involve sensitive data, and document handling needs to follow clear rules around access, edits, and retention. Secure document storage helps maintain that discipline without adding extra steps to daily work.
Version control plays a key role here. Changes stay traceable, older drafts remain available for reference, and records reflect how a document evolved over time.
Legal software also limits who can access documents, which reduces exposure and keeps confidential information contained. Together, these controls support reliable recordkeeping and make audits, reviews, and internal checks far easier to manage.
Improving Team Collaboration
Collaboration works best when everyone sees the same information at the same time. Cloud-based document management supports this by keeping files available anytime, anywhere.
Collaboration tools make it easier to manage documents efficiently throughout the document lifecycle. For example, a draft can move from one reviewer to the next with comments saved in place, while others can view progress without editing the file.
Remote access also matters a lot. With cloud solutions, team members can review, comment, or approve documents without being tied to the same location, which keeps work moving and reduces delays caused by handoffs.
Lowering Operational Risk
Operational risk usually builds up over time. For example, files get stored in different places, access rules blur, and important documents rely on habits rather than clear controls.
Legal document management software brings that risk back under control without complicating daily work.
Here’s how it helps in practice:
- Stronger data security: Advanced security features protect sensitive information and lower exposure to data breaches compared to open file servers.
- Controlled access to critical files: Permissions limit who can view or edit documents, which reduces accidental changes or unwanted access.
- Less dependence on physical documents: Digital systems avoid the loss, damage, and misplacement issues that come with paper files.
- Better visibility for legal compliance: Compliance tools track access and changes, which make reviews and audits easier to handle.
- One place for document handling: Centralized storage removes confusion caused by scattered folders and legacy systems.
Key Components of Good Legal Document Management
Good legal document management comes down to a few core elements:
1. Centralized Document Storage
Centralized document storage means case files and client files live in one system rather than being spread across desktops or personal folders. A legal DMS creates a single document management system that everyone uses as the source of record.
This setup affects how data management works day to day. Documents follow the same structure across matters, updates stay tied to the same file, and location stops being a variable.
Moreover, legal teams interact with documents through the system rather than managing storage decisions on their own, which keeps file handling consistent throughout a matter.
2. Version Control and Change Tracking
Version control and change tracking keep documents from drifting as they move through legal workflows. Each time someone edits files, the system records the update rather than creating disconnected copies. That history matters once multiple people are involved.
For example, a draft can go through internal review, client edits, and final approval without anyone wondering which version reflects the latest changes.
Key elements include:
- Clear version history: Shows how a document evolved and which version is current.
- Tracked edits: Records changes made during review so decisions stay visible.
- Restore options: Allows earlier versions to be recovered if needed.
- Integration with management tools: Keeps document updates aligned with the rest of the workflow.
This keeps documents stable as work progresses, even when revisions stack up.
3. Search and File Organization
Search and file organization shape how usable a modern legal DMS feels in daily work. A clear system helps documents stay easy to locate, even as volume grows and matters become more complex.
Key elements include:
- Document type categories
- Matter and case-based folders
- Consistent naming conventions
- Metadata and tagging fields
- Full-text search
- Filters for date, author, and status
Together, these lawyer tools support faster navigation through files and reduce reliance on personal filing habits.
4. Access Controls and Permissions
Not every document needs to be open to everyone. In legal departments, some files contain sensitive client data that only a few people should touch, while others are fine to share more widely.
Access controls handle that quietly in the background. You decide who can view a document, who can make changes, and who should leave it alone.
For instance, a working draft might stay editable for the core team, while a finalized version is locked down before it’s shared outside.
Keeping those boundaries clear helps protect data integrity and avoids awkward situations caused by the wrong level of access.
5. Audit History and Activity Tracking
Imagine reviewing a filing and realizing the language changed since the last time you looked at it. The question becomes simple and uncomfortable at the same time. Who made the change, and when did it happen?
Legal document management software answers that without guesswork. Activity tracking shows who opened, edited, or shared the same document and ties those actions to a clear timeline.
Plus, audit trails make it easy to review how relevant documents evolved and confirm what version was used at each stage. This kind of visibility matters when questions come up later, especially during reviews, disputes, or internal checks.
6. Retention and Recordkeeping Rules
Retention rules answer a basic question. How long do you keep documents, and what happens to them once a matter is done?
In many small law firms, those decisions get made on the fly, which usually means files stick around longer than needed or get handled inconsistently.
Clear recordkeeping rules take the guesswork out of it. Documents move from active work to archive on a predictable timeline, and outdated files get handled the same way every time.
This reduces manual processes and helps maintain operational efficiency without turning recordkeeping into a separate project.
Key elements include:
- Defined timeframes for keeping different types of documents
- Clear separation between active, closed, and archived matters
- Standard approaches to archiving files
- Rules for disposing of documents that no longer need to be retained
- Clear ownership over recordkeeping decisions
Bringing Legal Document Management Together With Briefpoint
Legal document management sets the foundation for how legal work actually gets done. When documents stay organized and easy to handle, everything downstream works better, from review to production to final delivery.
That foundation becomes especially important in discovery. Briefpoint builds on strong document management practices by turning productions and case files into structured, usable discovery responses.

With tools like Autodoc, teams can generate responses with citations, track changes, and maintain control over documents as they move through the discovery process. The result is less manual handling and fewer opportunities for confusion at a stage where accuracy matters most.
If discovery work still feels heavier than it should, it may be time to see how Briefpoint fits into your workflow.
Book a demo today to see how Briefpoint supports document-heavy litigation work.
FAQs About What Is Legal Document Management
What is a legal document management system?
A legal document management system is software used by law offices to store, organize, and track legal documents in one place. It helps manage files throughout a matter, keeps versions clear, and supports better legal organization without relying on scattered folders or inboxes.
What does document management do?
Document management supports how documents are created, reviewed, stored, and retrieved. In the legal industry, it helps reduce administrative overhead, keeps court filings and internal documents easy to locate, and works alongside tools like case management software and knowledge management software.
What is the role of a legal document manager?
A legal document manager oversees how documents are handled within a firm. That includes setting standards for storage, maintaining document templates, managing access, and supporting teams so document handling stays consistent and reliable.
What is an example of legal documentation?
Examples include contracts, pleadings, discovery materials, client correspondence, internal memos, and court filings. All of these documents play a role in client service, accuracy, and overall client satisfaction.
5 Legal Project Management Examples in Real Legal Work
5 Legal Project Management Examples in Real Legal Work
A single legal matter can involve ten small decisions before lunch. Who reviews first? Which draft is current? When does something actually need approval? None of that shows up in a case caption, but it shapes how the work moves.
Legal project management lives in those moments. Sometimes it’s handled in someone’s head. Sometimes it’s tracked in legal project management software. Most of the time, it sits somewhere in between.
In this guide, we look at how legal project management shows up in everyday work through real examples that reflect how legal teams manage matters when things get busy.
What Legal Project Management Looks Like in Practice
Legal project management can sound like a big, firm-wide initiative, but day to day, it usually shows up in smaller, very real ways.
A litigation matter has moving parts. A discovery response has its own timeline. A contract review turns into a mini project the moment multiple people get involved. Legal work rarely moves forward as one single task.
In practice, legal project management means recognizing those pieces and giving them some structure. You map out what needs to happen, decide who owns each step, and track progress as things move forward.
That might look like setting clear deadlines for discovery responses, outlining review steps for a contract negotiation, or organizing tasks tied to a regulatory filing.
Moreover, the legal project management process often runs quietly in the background. A paralegal manages document prep. An associate tracks revisions. A partner reviews milestones rather than chasing updates. All of that counts.
When people talk about how legal project management works, they usually mean this practical layer. Essentially, it helps teams manage legal projects without turning every matter into a formal project plan.
5 Common Legal Project Management Examples
Once you see legal work as a series of projects, these examples start to feel familiar. They show up in everyday matters, not special cases or firm-wide initiatives. Each one involves clear steps, multiple people, and deadlines.
Take a look for yourself:
1. Managing a Litigation Matter From Intake to Trial
A litigation workflow rarely moves in a straight line, but it does follow a familiar rhythm.
Intake kicks things off, then deadlines start stacking up fast. Someone on the legal team needs to decide what happens first, who’s responsible for each piece, and how the work stays on track as the case picks up speed.
As the matter moves forward, discovery, motions, and court filings each bring their own set of tasks. Many lawyers may step in at different points, which makes coordination a big part of the job. Good matter management keeps everyone aligned without turning every update into a meeting.
And when outside counsel is part of the picture, clarity matters even more. Clear roles, clear timelines, and clear ownership help legal services teams stay focused from intake through trial, even as things shift along the way.
2. Discovery Management and Written Discovery Workflows
If you’ve handled discovery more than once, you already know how quickly it can sprawl. A few requests land, and suddenly, half your time goes into keeping track of where things stand. That’s usually the moment discovery turns into a project of its own.
Legal project management shows up in the way you guide that work. Someone reviews the requests first, someone drafts, while someone checks the details before anything goes out the door.
When those roles are clear, the work feels lighter, even when deadlines stay tight and legal processes keep moving.
Most discovery work follows a familiar path:
- Reviewing incoming requests
- Assigning drafting and review tasks
- Tracking response deadlines
- Collecting and producing documents
- Cleaning up revisions before service
Written discovery adds extra pressure because every case looks similar on the surface but plays out differently in practice.
Resources like a discovery objections cheat sheet help legal professionals stay consistent when reviewing requests, flagging issues, and responding efficiently, while keeping final judgment with the legal team responsible for the outcome.
3. Handling Contract Review and Negotiation Projects
Contract review usually slows down for one reason: no one is quite sure where things stand. You may have a clean draft, open comments, and a pending decision all at the same time. Without a clear way to manage that flow, even simple legal matters start dragging.
Legal project management helps you stay oriented as negotiations unfold. It gives the work a sense of direction, so drafts move forward instead of circling. Law firm partners can step in at the moments that call for judgment, while the rest of the review keeps moving.
Legal project management tools support that rhythm by keeping context intact as timelines shift and negotiations stretch out. You spend less time untangling version history and more time pushing the agreement toward resolution.
4. Regulatory or Compliance Projects
Regulatory and compliance work often moves more slowly than expected, not because the rules are unclear, but because so many people are involved.
Deadlines come from outside the organization, requirements shift, and updates need sign-off from more than one group. In the legal industry, many law firms treat this work as ongoing, but each filing or review still functions like its own project.
Legal project management helps bring predictability to that process. Clear ownership and timelines lead to fewer surprises, even when regulations change midstream or feedback comes in late from other stakeholders. The main drivers stay visible, so the work keeps moving.
Regulatory and compliance projects often involve:
- Tracking filing deadlines and review periods
- Coordinating input from legal, compliance, and business teams
- Managing document revisions and approvals
- Keeping requirements aligned as guidance changes
With structure in place, these projects feel more controlled, even when external pressure sets the pace.
5. Internal Law Firm Operations and Process Improvements
Internal projects usually start with a realization and not a deadline. Intake feels inconsistent, and templates live in too many places. Work gets done, but no one would say the process feels clean. These are the issues a legal department notices first, long before clients ever do.
This is where legal project managers tend to step in. The focus shifts from closing a matter to fixing how work happens day to day. Project management techniques help turn informal fixes into decisions that stick, like standardizing intake or tightening review loops.
The payoff shows up later. Future projects feel easier to launch because the groundwork is already there. Fewer questions come up, and fewer exceptions need explaining.
Common Patterns in Legal Project Management
Once you step back and look at different legal projects side by side, some patterns show up again and again. They don’t depend on firm size or practice area. They come from how legal work naturally unfolds and how people respond when things get busy.
Most legal projects share a few common elements:
- Defined project phases: Work usually moves through recognizable stages, such as intake, execution, review, and closeout. Naming those phases helps teams see progress instead of reacting task to task.
- A clear project scope: Someone decides what is included and what is not. That boundary reduces confusion, especially when new requests surface midstream.
- A simple work plan: This doesn’t need to be formal. It can be as basic as knowing the next steps, owners, and deadlines.
- Clear expectations: Everyone understands their role and when input is needed, which cuts down on follow-up and rework.
- Consistency in approach: A legal project management professional often applies the same project management principles across different matters, which can create many benefits over time.
These patterns show that legal project management works best when it supports how teams already think and work, rather than forcing a rigid system into place.
How to Start Applying These Examples to Your Own Matters
You don’t need a full rollout or a new system to get value from legal project management. We’ve looked at concrete examples that already exist inside everyday legal work.
The next step is figuring out how to apply that same structure to your own matters, starting small and building from there. Here’s how:
Pick One Matter To Start
Start with a single matter that has a clear beginning and end. That keeps things manageable and makes it easier to see what’s working. A good example might be an RFP response with a fixed deadline or a contract review that involves more than one reviewer.
At the beginning, get the project team aligned on who owns each step and what needs to happen first. You don’t need a detailed plan. Even agreeing on review order and timing can change how the work feels.
Once that matter wraps up, you’ll have a clearer sense of what to repeat on the next project.
Clarify Ownership Early
Clarifying ownership early keeps work from stalling while people wait on each other. One person doesn’t need to do everything, but someone does need to be responsible for moving things forward.
For example, in a discovery response, one attorney may own the initial review, another handles legal drafting, and a third gives final sign-off. When that’s clear from the start, questions get answered faster, and revisions don’t bounce around unnecessarily.
Clear ownership gives the project team confidence to act without second-guessing, which keeps the matter moving even when timelines tighten.
Break Work Into Phases
Most legal matters already move in stages. So, breaking work into phases makes those stages visible and easier to manage for the in-house team.
Each phase has a purpose, a stopping point, and something concrete to review before moving on.
That usually includes:
- Defining the key deliverables: Clear outputs help everyone understand what needs to be completed in each phase.
- Setting project milestones: Milestones act as natural check-in points and keep momentum steady.
- Reviewing between phases: Brief pauses allow for deeper insights and adjustments before the next stage begins.
Set Expectations Around Timing
Timing usually causes problems when no one talks about it. You may assume a review will happen in a day, while someone else is planning for a week. That gap usually leads to follow-ups, rushed edits, and frustration.
It helps to say things out loud early. If a draft needs two rounds of review, agree on when each round should happen. If a partner’s sign-off affects the rest of the schedule, make that part of the conversation from the start. Those simple expectations change how the work feels.
Clear timing also keeps legal spend from creeping up. When work stretches longer than planned, budgets follow. Aligning on timing makes it easier to control costs and keep the budget in check without added pressure.
Use Tools Where They Add Value
Do you actually need a tool for this, or is it already working fine? That question helps keep things grounded. Legal project management software makes sense when it removes friction, not when it adds another place to check.
For example, having one place to see deadlines or review status can save time and make updates easier to share. That matters when client relationships depend on clear answers and steady progress.
If a tool helps you stay ahead of questions rather than reacting to them, it’s doing its job.
Adjust As The Matter Evolves
Legal work has a way of changing once it’s underway. New details come up, priorities shift, and timelines rarely stay exactly as planned.
Along the way, that usually looks like:
- Checking back on the plan to see what still makes sense and what needs to change.
- Making small course corrections early before timing or workload issues grow.
- Doing a brief post-project review to see what affected cost control and carry that insight forward.
Treating the plan as flexible keeps the work moving in step with what’s actually happening.
Bring Structure Into Work That’s Already Happening
Legal project management doesn’t require a reset of how you work. The examples in this guide show that structure already exists inside most legal matters. The shift comes from recognizing it and applying it more intentionally.
When ownership is clear, timing is discussed early, and work is broken into phases, projects feel easier to manage. At the same time, fewer surprises come up, and teams spend less time chasing status and more time focused on the work itself.

That approach becomes especially valuable during discovery, where volume, deadlines, and revisions stack up quickly. This is where tools that support your existing workflow can make a real difference.
Briefpoint helps legal teams manage written discovery by turning requests, productions, and case materials into draft responses with citations already in place. You still review, revise, and make judgment calls, but you’re no longer starting from a blank page.
For teams looking to bring structure to one of their biggest bottlenecks, Briefpoint fits naturally into a legal project management approach.
FAQs About Legal Project Management Examples
What does a legal project manager do?
A legal project manager focuses on how legal work gets done. They help define scope, assign ownership, track progress, and surface risks early. The role often includes coordinating with attorneys, clients, and outside law firms so matters stay organized and predictable.
What are the 5 C’s of project management?
The 5 C’s commonly refer to clarity, communication, coordination, control, and closure. Together, they help teams set expectations, follow a plan, manage change, and capture lessons learned once the work wraps up.
What are the legal aspects of project management?
Legal project management has to account for confidentiality, professional responsibility, budgeting, and risk management. It also involves aligning work with the client’s business goals while staying compliant with legal and ethical standards.
How does legal project management improve communication?
It creates a shared communication plan that defines who needs updates, when decisions are required, and how information flows. That clarity reduces confusion and helps teams respond faster as matters evolve.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
What Is Legal Project Management?
What Is Legal Project Management?
Legal work has always required coordination.
What’s changed is the pace and volume of work, along with higher expectations around transparency, cost, and turnaround. Managing all of that through emails, spreadsheets, and memory alone gets harder over time.
Legal project management grew out of that pressure, not as a rigid system or a one-size-fits-all framework, but as a practical way to bring structure to work that already demands planning and follow-through.
And for many teams, legal project management software plays a supporting role by helping make plans visible and work easier to track as matters move forward.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how legal project management fits into real legal work, when it becomes useful, and how teams can adopt it in the most efficient way possible.
What Is Legal Project Management?
Legal project management isn’t a tightly defined concept with a single rulebook (at least not yet). Most people in law didn’t learn it in school, and many teams use parts of it without ever calling it that.
At a practical level, it’s a way to bring order to legal work that already feels complex. You plan a matter, break the work into clear steps, assign responsibility, and track progress as things move forward. The goal is to make sure everyone knows what’s happening and what comes next.
If you work in a law firm, this probably sounds familiar. You already manage deadlines, coordinate people, and respond to changes mid-matter. Legal project management puts a structure around those habits so they’re easier to repeat and easier to improve.
For teams that implement legal project management, the shift often feels subtle at first. Fewer surprises. Clearer communication. Less time spent figuring out status and more time actually doing the work. It doesn’t replace legal judgment or experience; it supports them.
At the end of the day, legal project management helps legal services run with more clarity and consistency, especially as matters grow larger, faster, or more collaborative.
How Legal Project Management Applies to Legal Matters
Legal matters rarely follow a neat script. Something changes, a deadline shifts, a new request lands in your inbox, and suddenly the plan needs adjusting. Legal project management helps you keep your footing when that happens.
At the matter level, it gives you a clear way to organize work from start to finish. You know what’s coming up, who owns each task, and how the pieces connect. That visibility makes it easier to manage client expectations and stay calm when work picks up.
Here’s how it tends to play out in real situations:
- Litigation matters: Major litigation phases like pleadings, discovery, and motions are mapped early, so even complex matters feel easier to track as they move forward
- Transactional matters: Reviews, approvals, and closing steps follow a clear order, which cuts down on confusion and helps everyone stay aligned as timelines tighten
- Ongoing advisory work: Repeat work gets documented and refined over time, leading to steady process improvement without adding extra steps
Across the legal industry, teams use this approach to build better organization and efficiency. As habits develop, work becomes more predictable, communication improves, and law firm success becomes easier to sustain without constant fire drills.
Does Your Team Need Legal Project Management?
Some teams look for legal project management after a problem shows up. Others notice patterns that quietly slow work down as time goes on.
If any of the situations below feel familiar, it may be worth taking a closer look:
- Deadlines feel harder to track than they should: Important dates live in too many places, and staying on top of them depends on memory rather than a shared system.
- Work ownership feels unclear: Tasks get done, but no one can easily say who owns what or what’s coming next.
- Status updates take more time than the work itself: You spend a lot of time answering emails or meetings that exist mainly to figure out progress.
- Matters expand without clear boundaries: New requests get added midstream, timelines stretch, and priorities shift without a clear plan to adjust.
- Resources feel stretched even on routine matters: The team works hard, yet capacity feels tight because effort isn’t always directed where it matters most.
Legal project management helps create visibility around work so teams can make better decisions earlier. It gives structure to work that already exists, which should make it easier to spot issues before they grow and help teams use their resources with more intention.
The Key Components of Legal Project Management
Legal project management works best when a few core pieces stay consistent across matters. In other words, you need clear building blocks that help work move forward without confusion.
Here are the key components that form the foundation:
Planning and Scoping
Planning and scoping are really about getting everyone on the same page before the work takes off. It’s the moment where you step back and ask, what does this matter actually require, and where do the limits sit?
For attorneys, that usually means talking through the client’s specific needs, the outcome you’re working toward, and the key steps along the way. Nothing here needs to be overly formal.
Some teams turn this into a light program that they reuse across matters. A few simple techniques, like outlining phases or flagging early assumptions, can make a noticeable difference.
Keep in mind that when the scope is clear from the start, changes feel manageable and the work stays easier to control as things evolve.
Task Ownership and Accountability
Task ownership keeps work moving without constant check-ins. When everyone knows who owns what, decisions happen faster and follow-ups feel natural rather than awkward.
On a matter team, this usually starts with clarity from leadership. Tasks get assigned to a specific person, not a group, so responsibility doesn’t drift. That doesn’t mean working in silos, though. It means the legal team knows exactly who to go to for updates or decisions.
Project managers often help reinforce this structure, especially on larger matters, but the same idea works on smaller teams too.
For example, during legal discovery, one attorney may own document review deadlines while another handles drafting responses. Each person knows their role, and the rest of the team can plan around that work with confidence.
Timelines and Milestone Tracking
Timelines and milestones give structure to work that can otherwise feel open-ended. For lawyers and other legal professionals, they create a shared sense of pace across matters and practices.
Rather than tracking every small task, teams focus on meaningful checkpoints that show progress and signal what’s coming next.
Common milestones include:
- Initial case assessment completed
- Discovery requests sent
- Discovery responses finalized
- Key motions drafted
- Deal documents approved
- Closing completed
When milestones are visible, teams can adjust earlier, coordinate better, and keep work moving.
Communication and Visibility
Imagine this scenario: you’re halfway through a matter, and someone asks for a status update. You know the work is moving, but pulling together a clear answer takes longer than it should.
That’s usually a visibility problem and not a work problem.
A good legal team or law firm’s communication keeps everyone aligned without constant check-ins. When progress is easy to see, conversations shift from “where are we?” to “what’s next?”
Technology often helps support this, especially when many clients or multiple teams are involved. Shared views into timelines and tasks reduce long email chains and repeated questions. The same applies when working with outside law firms, where clarity keeps collaboration smooth.
Legal project managers play an important role here. They help set expectations around updates, keep information flowing, and make sure key details stay visible as matters move forward.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation comes into play when work starts piling up, and choices have to be made.
Who handles this task? How much time makes sense? Which lawyer tools actually help rather than slow things down?
When those decisions are clear, the budget stays easier to manage, and legal spend feels more intentional.
Teams usually think about resource allocation in a few practical ways:
- Who does the work: Assigning tasks based on skill level so effort matches the complexity, and costs stay in check.
- How time is used: Making room for work that truly moves the matter forward.
- Which tools support the process: Choosing tools that reduce manual effort and support consistency.
- How costs add up: Keeping an eye on decisions that affect spend over the life of the matter.
Risk and Change Management
Legal matters change. New facts surface, priorities shift, and timelines adjust. Risk and change management give you a way to stay steady when that happens.
Managing risk starts with awareness. Spotting potential risks early makes legal challenges easier to handle before they disrupt the entire matter.
Risk management doesn’t eliminate uncertainty, but it helps teams respond with intention rather than urgency.
Teams often focus on a few core areas:
- Identifying potential risks early: Flagging issues that could affect scope, timing, or outcomes.
- Assessing impact: Understanding how changes affect deadlines, workload, and expectations.
- Adjusting plans openly: Updating timelines and responsibilities so everyone stays aligned.
- Documenting decisions: Keeping a clear record of changes to support consistency and accountability.
How to Get Started with Legal Project Management
Getting started with legal project management doesn’t require a full process overhaul. Small, intentional steps make a real difference and help teams build habits that stick.
Try to focus on these key areas as you begin:
1. Assess Current Workflows
Before changing anything, take a step back and look at how work actually flows today. Not how it’s supposed to work on paper, but how it really moves from one person to the next.
Most teams already have patterns in place, even if they feel a little chaotic.
For example, a business matter might bounce between intake, review, and approvals with no clear handoff. When timelines slip, everyone may expect faster turnaround, yet no one can point to where things slowed down.
Seeing those patterns clearly gives you a realistic starting point and helps you decide what needs attention first.
2. Define Clear Matter Goals
Clear matter goals give direction to the work from day one. Without them, it’s easy for tasks to pile up without a shared sense of purpose.
Start by asking a few simple questions. What does success look like for this matter? What needs to be delivered? What does the client or business expect at the end? When those answers are clear, decisions become easier, and work stays focused.
Defining goals also helps teams deliver greater value. Time and effort are spent on what’s actually important, rather than side tasks that don’t move the matter forward. Even a brief goal statement can anchor the entire project and keep everyone aligned as things change.
3. Start With Simple Planning Tools
You don’t need complex systems to get started. Simple tools often work best, especially early on, and many legal project management professionals rely on lightweight planning to keep work visible.
Common examples include:
- Matter timelines
- Task checklists
- Shared spreadsheets
- Basic project boards
- Calendar-based trackers
Remember: The goal is clarity and not complexity. When planning tools are easy to use, teams actually stick with them.
4. Assign Ownership Early
Things tend to run more smoothly when ownership is clear from the start. When roles get defined early, the team spends less time sorting out who should handle what once deadlines creep closer.
Picture a matter with several stakeholders involved. One person takes charge of client communication. Another focuses on legal drafting and review.
Everyone knows their lane, which makes it easier to collaborate and assist each other when work overlaps.
5. Build Consistent Communication Habits
You’ve probably been on a matter where updates came in bursts. Nothing for days, then a flood of messages all at once. That pattern makes it harder than necessary to stay oriented.
Consistent communication fixes that. When updates come at expected moments, you stop wondering where things stand. This is especially helpful when working with outside counsel, since everyone operates with different rhythms and assumptions.
Within the legal profession, small habits tend to work best. These might include a quick status note at the same point each week, clear next steps after a call, or one place to check progress.
Those routines don’t add work, but they do bring many benefits, including fewer interruptions and calmer coordination as matters move along.
6. Review and Adjust Over Time
Regardless of how well a matter is planned, things will change. That’s why reviewing progress along the way helps you spot what’s working and what needs a tweak before small issues grow.
For example, after a discovery phase wraps up, a team might notice that reviews took longer than expected. That insight can shape how timelines are set for the next matter.
Or after closing a deal, you may realize certain approvals always slow things down and adjust the sequence next time.
These quick check-ins don’t need to be formal. A short conversation after key milestones is often enough to carry lessons forward and make the next matter run a little smoother.
Find Out How Briefpoint Fits Into Legal Project Management
Legal project management works best when the structure supports the way legal workflows actually happen. Clear planning, ownership, timelines, and communication all count, but they still rely on execution. That’s often when the right tools become part of the conversation.

Discovery is a good example. It’s deadline-driven, detail-heavy, and often repeated across matters.
Briefpoint supports legal project management by bringing consistency and clarity to discovery responses, with the central goal of helping teams stay organized without adding extra process.
Briefpoint’s core belief is that when drafting and formatting take less time, it’s easier to plan work, assign ownership, and keep matters moving on schedule.
Legal project management doesn’t require perfection. It improves through small, practical changes paired with tools that fit naturally into your workflow.
So, if discovery work keeps slowing matters down, take a closer look at how Briefpoint can support your process.
FAQs About Legal Project Management
What do legal project managers do?
Legal project managers help organize legal work so matters stay on track. They focus on planning, timelines, coordination, and communication, which allows attorneys to concentrate on legal judgment. Strong project management skills help them support teams without disrupting existing workflows.
What is the overview of legal project management?
Legal project management is a structured way to plan and manage legal matters from start to finish. It brings clarity around goals, responsibilities, and progress, which supports better coordination and more consistent client service.
Is legal project management useful for a legal professional seeking new skills?
Yes. A legal professional seeking to expand their role often finds legal project management valuable. It builds skills that support leadership, coordination, and decision-making across different types of matters.
Do you need formal training to work in legal project management?
Formal training programs or a course can be helpful, especially for those moving into dedicated project roles. That said, many teams start by applying basic concepts and improving quality through experience over time.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
11 Best Legal Tech Companies of 2026
11 Best Legal Tech Companies of 2026
Legal work today comes with growing expectations around speed, accuracy, and cost, while many of the tasks that consume the most time still rely on manual effort and repeatable processes.
As firms handle larger volumes of discovery, manage more complex matters, and respond to clients who expect faster turnaround, technology has become part of the everyday reality of legal practice.
The challenge is no longer finding legal tech, but choosing tools that actually make work easier once they are part of a firm’s workflow.
In this article, we’ve compiled a list of the 11 legal tech companies worth attention in 2026, each recognized for helping legal teams work more efficiently, stay consistent, and spend more time on substantive legal work.
1. Briefpoint.ai
Briefpoint is a litigation-focused legal tech company built to take the most time-consuming parts of written discovery off your plate: discovery document preparation.
Drafting discovery responses, mapping productions, and managing Bates citations often eat up hours of attorney and paralegal time, even though much of the work follows repeatable patterns. And that’s just one part of the tedious discovery process.
Briefpoint addresses that problem with purpose-built automation designed specifically for real-world litigation workflows.

The platform includes features like Autodoc, which helps teams move from raw productions and discovery requests to cited, court-ready responses far faster than traditional manual review.
And with Briefpoint’s generative AI, legal teams can draft discovery response documents in minutes. These include, but are not limited to:
- Requests for admission
- Requests for production
- Interrogatories
Key Features
- Automated discovery drafting: Generates objection-aware requests for admission, requests for production, and interrogatories based on complaints and case details.
- Response drafting with built-in objections: Pre-fills consistent objections and response structures that firms can customize across matters and practice areas.
- Client response collection (Briefpoint Bridge): Sends plain-English questions to clients, collects answers securely, and inserts them directly into Word-ready discovery drafts.
- Autodoc production automation: Turns productions and case files into Bates-cited discovery responses and ready-to-serve production packages with page-level citations.
- Microsoft Word–first output: Produces fully captioned, editable Word documents for requests, responses, and productions.
- Firm-wide consistency controls: Helps standardize objections and drafting practices across teams and offices.
- Security and compliance: SOC 2 Type II certified with safeguards designed to protect confidential work product.
Briefpoint saves legal professionals thousands of dollars every year. More importantly, lawyers and paralegals can spend the extra time on more impactful and engaging work.
2. Clio
Clio has long been the answer for law firms and legal professionals looking for a simple yet effective practice management system.

Source: G2
Its comprehensive suite is remarkably user-friendly and accessible to a broad range of professionals, regardless of their technical expertise.
As a cloud-based solution, Clio also offers the flexibility required in today’s legal environment and allows work to be conducted from virtually anywhere. This adaptability is especially valuable given the increasing shift towards remote and flexible working arrangements.
Key Features
- Case management: Organizes client matters, documents, and communications in one centralized platform.
- Time tracking & billing: Tracks billable hours and generates invoices. Also, the platform integrates directly with payment processing tools.
- Document management: Stores, organizes, and shares legal documents securely with version control.
- Client intake & CRM: Streamlines client onboarding with customizable intake forms and contact management.
- Task and workflow automation: Automates routine legal workflows to improve efficiency and reduce administrative tasks.
- Secure communication: Provides encrypted messaging and client portals for confidential interactions.
- Integrations & API access: Connects with legal tech tools like QuickBooks, Microsoft 365, and Zoom.
3. Everlaw
Everlaw is a global leader in advanced discovery and litigation support solutions.
Its platform is known for merging cutting-edge technology with an intuitive design to manage the complexities of legal document analysis and case preparation efficiently.
Source: G2
What’s also great about Everlaw is how it champions team collaboration. The platform includes tools for annotation, tagging, and sharing documents, which allows team members to work together regardless of their physical location.
Key Features
- Predictive coding: Uses machine learning to prioritize and categorize documents, speeding up the review process.
- AI-powered document review: Automates document analysis, which helps legal teams quickly identify relevant information.
- Advanced search and filtering: Offers powerful search capabilities with Boolean operators and AI-driven suggestions.
- Redaction and annotation tools: Allow users to highlight, redact, and comment on key information directly within documents.
- Case timeline visualization: Helps legal teams track case progress and connect key events through interactive timelines.
- Automated transcription: Converts audio and video files into searchable text for faster review.
4. LawVu
LawVu combines multiple aspects of legal operations into one convenient platform. This approach is meant to address the specific needs of in-house corporate legal departments and improve the efficiency, collaboration, and overall management of legal matters.
Source: G2
Plus, LawVu’s platform includes advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, which allow legal services to get a clear grasp of their operations, assess performance, and make data-driven decisions to improve their services.
Key Features
- Matter management: Centralizes all legal matters, documents, and communications in one platform.
- Contract lifecycle management: Tracks contracts from drafting to execution with automated workflows.
- Spend management: Monitors legal expenses, invoices, and budgets to control costs.
- Knowledge management: Stores and organizes legal documents, templates, and historical case data.
- Task & workflow automation: Streamlines legal processes with automated task assignments and approvals.
- Collaboration tools: Enable secure communication and collaboration between in-house teams and external counsel.
5. LeanLaw
LeanLaw Billing Software is a smart solution for smaller and mid-sized law firms looking to mesh their legal practice needs with solid accounting.
Source: LeanLaw.com
By teaming up with QuickBooks Online, LeanLaw taps into powerful accounting tools and makes the whole financial side of running a law firm (from keeping track of billable hours to keeping an eye on the firm’s finances) a lot smoother and more straightforward.
LeanLaw also offers a package for organizing client details and internal resources, so everything you need is just a few clicks away.
Key Features
- Time tracking: Tracks billable hours with real-time timers and manual entry options to help firms in the legal profession meet growing demand without losing billable time.
- Automated legal billing & invoicing: Generates LEDES-compliant invoices and integrates with QuickBooks for accurate, consistent billing.
- Trust accounting: Manages client trust accounts with built-in compliance safeguards aligned with common accounting requirements.
- Expense tracking: Logs case-related expenses and links them directly to client invoices.
- Revenue & compensation reports: Provides visibility into firm profitability and attorney compensation as workloads increase across the legal profession.
- Matter management: Organizes cases, documents, and client information in one centralized system.
6. Smokeball
Smokeball is legal practice management software geared specifically towards small law firms and solo practitioners. It focuses on streamlining repetitive legal processes, which can reduce the time lawyers spend on administrative work.

Source: G2
Billing and time tracking are other areas where Smokeball excels. It automatically tracks time spent on each task and integrates it with its billing system, simplifying the invoicing process and ensuring that no billable hour goes unrecorded.
Key Features
- Case and matter management: Centralizes case files, client communications, and documents in one platform.
- Document automation: Generates legal documents quickly using customizable templates and client data.
- Task and workflow automation: Streamlines legal workflows with automated task assignments and reminders.
- Firm insights & reporting: Provides real-time analytics on firm performance, revenue, and law firm productivity.
- Secure client communication: Offers a built-in client portal for messaging and document sharing.
7. Ironclad
Ironclad is a complete and scalable solution for teams drowning in contracts and looking for a better way to get things done.
Source: G2
The contract management tool automates the creation, execution, and management of contracts. In addition, this tool can integrate with other tools you’re already using.
Its integration capabilities make sure that contract management becomes a cohesive part of the broader business ecosystem and leads to smoother workflows across departments.
Key Features
- AI-powered contract review: Uses AI to analyze contracts, identify risks, and suggest edits.
- Automated contract generation: Creates contracts using templates and pre-approved clause libraries.
- E-signature integration: Integrates with DocuSign and other e-signature platforms for seamless contract execution.
- Real-time collaboration: Allows legal, sales, and procurement teams to collaborate on contracts within the platform.
- Contract repository & search: Stores all contracts in a secure, searchable database with advanced filtering.
- Compliance & audit trails: Tracks all contract changes and approvals for compliance and reporting.
8. MyCase
MyCase is a legal practice management software that simplifies legal workflows and keeps them running smoothly. It tackles everything from case management and client communications to billing and time tracking into one neat platform.
Source: G2
This means lawyers can spend less time handling different tools and more time focusing on their clients’ needs. With MyCase, everything you need to run your law practice is right there in one easy-to-use interface.
MyCase is also great when it comes to keeping clients in the loop. It offers secure messaging, updates on case progress, and easy online payment options, which help law firms improve their client relationships.
Key Features
- Case management: Organizes case details, deadlines, and documents in a centralized system.
- Document automation: Creates, stores, and manages legal documents with customizable templates.
- Time tracking and billing: Logs billable hours, generates invoices, and integrates with online payment processing.
- Secure client messaging: Provides a built-in client portal for encrypted communication and case updates.
- Calendar and task management: Schedules meetings, tracks deadlines, and assigns tasks to team members.
- Online payment processing: Allows clients to pay invoices easily through credit cards or ACH transfers.
- Reporting and analytics: Offers insights into firm performance, revenue, and case progress.
- Mobile access: Enables lawyers to manage cases and communicate with clients on the go.
9. CoCounsel
CoCounsel, powered by Casetext, is another innovative legal tech tool. This AI legal assistant is groundbreaking for several reasons, notably its ability to offer legal support across a range of tasks that traditionally require hours of human effort.

Source: Thomsonreuters.com
Powered by Casetext’s extensive legal database, it leverages the latest in AI legal technology to fine-tune its capabilities and offer more personalized and accurate assistance over time.
Key Features
- AI-powered legal research: Uses advanced legal AI to quickly find relevant case law, statutes, and legal precedents.
- Automated contract review: Analyzes contracts, flags risks, and suggests revisions to ensure compliance.
- Deposition preparation: Summarizes depositions, highlights key testimony, and extracts important details.
- Litigation strategy assistance: Provides AI-driven insights to help lawyers craft stronger legal arguments.
- Legal document analysis: Reviews legal documents for inconsistencies, missing clauses, and potential errors.
- Secure cloud-based storage: Keeps all legal research, documents, and case materials organized and accessible from anywhere.
- Real-time collaboration: Allows legal teams to work together on case analysis, research, and legal document review.
- Integration with legal tools: Connects with existing case management and document automation software.
10. UniCourt
UniCourt is a legal tech service that simplifies how law firms get their hands on and use legal data. It’s a go-to resource for law firms, businesses, and anyone who needs quick access to court records and insights into legal trends.
Source: UniCourt.com
The best feature of UniCourt is how it brings all kinds of legal data together under one roof. Whether you’re keeping tabs on a specific case or trying to spot trends in litigation, UniCourt lets you do it all without the need to jump between different databases.
Aside from accessing data, UniCourt helps you manage it better. You can set up alerts to track cases automatically, so you’re always in the loop with real-time updates without constantly checking in manually.
Key Features
- Automated court data access: Retrieves real-time case data from federal and state courts.
- Legal research & analytics: Provides AI-driven insights into case law, dockets, and litigation trends.
- Case tracking & alerts: Notifies users of case updates, filings, and procedural changes.
- API & data integration: Connects court records with legal and business intelligence platforms.
- Docket management: Centralizes court dockets for easy organization and access.
- Business & litigation intelligence: Identifies patterns in litigation to help firms assess risks and opportunities.
- Document retrieval: Automates access to pleadings, motions, and other legal filings.
11. Justpoint
Justpoint is a legal tech startup that combines AI and scientific research to spot harmful products and undisclosed adverse effects earlier, then helps people who may have been harmed understand their legal options.
Source: Justpoint.com
Victor Bornstein, the co-founder and CEO, trained in biomedical sciences, brings a research-first mindset to the company’s work, focusing on how data and science can surface risks tied to everyday consumer products sooner.
He co-founded Justpoint to apply innovation and an AI-driven solution to uncover harm earlier and help move people closer to justice.
Rather than selling a standalone tool to plaintiff law firms, Justpoint runs investigations, reviews records and research, and routes viable claims into litigation through Justpoint Law and partner law firms.
Key Features
- Legal AI-assisted risk detection: Uses large-scale analysis of research, safety signals, and real-world data to flag potential dangerous products (e.g., harmful drugs) and adverse effects.
- Medical record review and case viability screening: Evaluates medical records and related documentation to assess medical and legal viability.
- Scientist-led investigations: The company employs scientists and pairs AI output with reviews from experts across areas like toxicology, pharmacology, and epidemiology.
- Plaintiff intake and claim matching: Helps affected individuals submit information and get routed into an appropriate legal path.
- Litigation pathway through Justpoint Law and partners: Moves validated matters toward filing and case progression through its legal arm and partnered firms.
- No upfront fees for plaintiffs: Operates on a pay-only-if-you-win approach, covering case costs up front.
Why Briefpoint Sets the Standard for Discovery Automation
Legal discovery is often the most time-consuming part of litigation, not because it requires deep legal judgment at every step, but because the same tasks repeat again and again.
Drafting requests, preparing responses, tying productions to specific requests, and handling Bates numbers can quietly take over an entire case.

That’s the gap Briefpoint was built to address. It focuses on the work that slows teams down and clears it out of the way.
Briefpoint automates large portions of discovery drafting and production preparation so litigation teams can move faster and stay consistent across matters.
Reviews stay in human hands, timelines become easier to manage, and discovery stops feeling like the part of the case that throws everything off track, especially in matters with heavy document volume.
Curious what that looks like in practice?
FAQs About Legal Tech Companies
What is legal tech, and how does it benefit legal professionals and their clients?
Legal tech refers to the use of technology and software to provide legal services and support the operation of law firms and legal departments. Legal tech benefits legal professionals by streamlining workflows, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional legal processes, and enhancing the accuracy of legal documents and research.
For clients, legal tech can lead to quicker resolutions of legal matters, improved access to legal services, and, often, lower costs.
Can legal tech replace lawyers?
While legal tech software improves the efficiency and effectiveness of legal services, it is not designed to replace lawyers. Instead, it serves as a tool to assist lawyers in their work.
Technology can automate repetitive tasks and manage large volumes of data, but the nuanced judgment, ethical considerations, and client advocacy provided by human lawyers are beyond its current capabilities.
What are the top legal tech companies?
Top legal tech companies are those solving real operational problems across the legal industry, from discovery and practice management to contract workflows and litigation intelligence. These companies tend to set a market standard by focusing on efficiency, accuracy, and measurable outcomes rather than novelty alone.
What is a legal tech firm?
A legal tech firm builds technology designed to support or improve how legal work gets done. Some focus on software used by law firms, courts, or in-house teams, while others operate hybrid models that combine technology with legal services.
Depending on the focus, a legal tech firm may help lawyers produce documents faster (like demand letters and legal motions), manage data at scale, or support specific practice areas such as personal injury or litigation-heavy matters.
How is AI being used in legal tech, and what are its limitations?
AI in legal tech is commonly used to analyze large volumes of documents, extract information using natural language processing, and assist with drafting or review tasks through custom large language models. These tools can speed up routine work and surface patterns that would be difficult to find manually.
However, AI still requires human oversight. Legal judgment, ethical considerations, and context-specific decisions remain critical.
How can legal drafting software benefit an international law firm?
Legal drafting software streamlines corporate and transactional issues by automating contract creation, compliance filings, and other essential documents. This reduces manual effort, ensures consistency across jurisdictions, and improves efficiency.
How does an AI legal assistant support day-to-day legal work?
An AI legal assistant helps legal teams handle large volumes of information faster by organizing and reviewing materials such as medical data, police reports, and case documents. For example, in matters tied to product liability or broader public health concerns, an AI legal assistant can surface timelines, flag missing records, and group related evidence to support early case assessment.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.
Best AI for Legal Documents: Top 7 Tools for 2026
Best AI for Legal Documents: Top 7 Tools for 2026
The best AI for legal documents makes legal work easier, to say the least. Yet, plenty of law firms are still hesitant to jump on board.
Some worry about accuracy, while others don’t want to change the way they’ve always done things. But the reality is, AI isn’t replacing lawyers. Rather, it’s taking tedious work off their plates.
Whether you’re running a solo practice or handling documents in an in-house legal department, the right AI can save time and let you focus on more important legal work.
Not sure where to start? This guide breaks down the best AI tools for legal documents so you can find the right tool to fit your workflow.
Types of AI Tools for Legal Documents
First things first, let’s talk about the different types of AI tools for legal documents. Not all legal AI tools do the same thing.
Here are the main types of AI tools, per the process they cover:
- Legal document drafting: Creates pleadings, discovery documents, contracts, and other legal paperwork based on templates and case details. It expedites the drafting process while maintaining accuracy.
- Contract drafting: These tools help create legal documents using templates and user inputs, which saves lawyers hours of manual work.
- Document review: Speeds up analysis by identifying risks, missing clauses, and inconsistencies, similar to how legal professionals review documents.
- Legal research: Finds relevant case law, statutes, and regulations quickly to cut down the time spent on legal research.
- E-signature and contract management: Simplifies contract signing, tracking, and storage to make sure deadlines aren’t missed.
- Litigation support: Assists with case analysis, summarizing legal documents, and predicting case outcomes during litigation workflows.
Each of these tools plays a role in making legal work more efficient and less prone to errors. Of course, the right tool depends on what you need, whether it’s drafting, reviewing, or managing other legal documents.
Why Should You Use Legal AI Tools for Legal Documents?
Aside from speeding up work, legal AI tools improve accuracy, compliance, and overall efficiency.
Let’s go over why you should have them in the first place.
Speeds Up Document Drafting
Drafting legal documents takes time, but AI makes it a whole lot faster. Instead of starting from scratch every time, lawyers can generate complete, well-structured documents in minutes.
For example, AI legal drafting tools can pull in key details, suggest relevant clauses, and format everything properly to cut down on repetitive work.
Take Briefpoint, for example. It automates legal drafting by pulling case details and structuring them into polished documents. That means less time spent on manual entry and more time focusing on the actual case.
With tools like this, lawyers don’t have to get stuck in paperwork; they can move through their workload faster and more efficiently.
Book a demo to see it firsthand!
Reduces Human Errors
Small mistakes in legal documents can create big problems. Luckily, AI helps catch those issues early, before they turn into something you have to clean up down the road.
When legal workflows rely heavily on manual processes, it’s easy for details to slip through. This is especially true when you’re reviewing long or repetitive documents.
AI solutions step in as a second set of eyes, scanning legal information carefully and flagging things that don’t line up. You still make the final call, but you’re not starting from a blank slate every time.
AI can help spot issues like:
- Inconsistent terminology
- Missing key clauses
- Formatting mistakes
- Duplicate or conflicting sections
- Incorrect dates or names
- Ambiguous language
- Non-compliant contract terms
However, it’s still important to think of AI-generated answers as support and not a substitute. They help surface potential problems faster, so your review time goes toward judgment and strategy, not hunting for avoidable errors.
Improves Compliance With Legal Standards
Staying compliant in the legal field takes constant attention. Rules change, expectations shift, and even experienced teams can miss details when they’re working through documents quickly.
AI helps reduce that risk by acting as a steady backstop during review.
Many tools use machine learning trained on legal terminology to spot clauses, language, or structures that may fall outside current standards.
Rather than replacing your judgment, they highlight areas worth a closer look, particularly in long contracts or documents that follow similar patterns.
For example, some contract management tools flag terms that don’t align with regulatory requirements or point out language that may need updating based on recent changes. That saves you from having to comb through every page, line by line, just to confirm compliance.
Again, you still stay in control of the final decision, but AI helps surface potential issues earlier.
Saves Costs on Administrative Tasks
Nobody wants to waste time on paperwork, and AI helps cut down on it. By handling routine tasks like legal drafting and data entry, AI lets law firms spend less on admin work and more on what really matters.
For example, AI can auto-fill forms, generate standard documents from templates, and organize case files without anyone having to do it manually.
That means fewer billable hours lost to repetitive work and more time for legal teams to focus on clients.
Supports Legal Research and Case Preparation
Some AI tools can scan thousands of past cases, legal precedents, and regulations in seconds to pull out the most relevant information. Many rely on generative AI layered on top of a large legal database, which helps surface results faster than traditional search alone.
That speed makes a real difference when you’re building arguments under tight deadlines. Rather than spending hours flipping through legal texts, you can review summaries of key cases, spot patterns across rulings, and zero in on the authorities that hold the most weight.
And with quicker access to the right information, case preparation feels more focused. Less time goes into searching, and more time goes into strategy, analysis, and making informed decisions.
Keeps Documents Organized and Accessible
Lastly, AI helps by sorting, categorizing, and tracking legal files so everything stays organized.
With AI software, contracts, case files, and agreements are easy to search and retrieve. Some platforms even tag documents based on keywords, client names, or terms. Automated reminders also help legal teams stay on top of deadlines.
Top 7 AI Tools for Legal Documents
All of those benefits sound good in theory, but they only matter if the tools actually hold up in day-to-day legal work. The real difference comes down to how well an AI tool fits into your workflow and supports the way you already practice.
Below are some of the best AI tools for legal documents:
1. Briefpoint
Briefpoint is an AI-powered discovery platform designed for the part of litigation that tends to consume the most time, which is most often drafting and responding to discovery.
If your work involves propounding discovery requests, reviewing responses, and preparing Bates-numbered productions, Briefpoint brings those steps into one cohesive workflow that matches how discovery actually gets done.

Rather than drafting requests for admission, requests for production, and interrogatories from scratch or spending days organizing productions, you can let Briefpoint handle the repetitive structure while you stay focused on substance and strategy.
The platform applies jurisdiction-ready formatting, standard objections, and properly structured responses, so discovery keeps moving.
If discovery shows up often in your matters, Briefpoint takes hours of repetitive work off your plate and replaces it with a review-first process you can rely on from case to case.
Key Features
- Propound discovery from a complaint: Upload a complaint, and Briefpoint automatically generates tailored interrogatories, RFAs, and RFPs. Each request is written to avoid common drafting issues like ambiguity or assuming facts.
- Automated discovery response drafting: Upload opposing counsel’s discovery requests, and Briefpoint identifies court details, parties, set numbers, and local formatting rules. Responses are structured automatically, with standardized objections applied where appropriate.
- Client response collection in plain English: Briefpoint Bridge converts interrogatories into plain-language questions and sends them to clients through a secure portal. Clients respond directly in their browser, and answers flow back into Word-ready drafts.
- Word-ready documents: All discovery responses export as properly formatted Word documents, complete with captions, numbering, and objections. Final review and edits happen where attorneys already work.
- Autodoc: Autodoc extends Briefpoint’s discovery workflow into document production. Upload RFPs and case files, and Autodoc locates responsive documents for each request and generates written responses with page-level Bates numbering.
- Security and compliance: Briefpoint is SOC-2 certified, encrypts data in transit and at rest, and keeps client data siloed per account. Uploaded materials are never used to train Briefpoint or third-party models.
Pros
- Handles both propounding and responding to discovery
- Produces jurisdiction-ready RFAs, RFPs, and interrogatories
- Cuts discovery drafting and production time from days to minutes
- Generates Bates-cited responses and ready-to-serve productions
- Keeps attorneys in control with Word-first editing and verification
If you want a full tour of Briefpoint, book your free demo today!
2. CoCounsel by Casetext
CoCounsel is an AI-powered legal document assistant that helps lawyers with research, contract review, and document analysis.
Developed by Casetext, it automates time-consuming legal tasks that would otherwise require significant manual effort.
Source: G2
With features like document summarization, deposition preparation, and contract analysis, CoCounsel functions as an AI-powered document assistant trained on large language models designed for legal workflows.
It processes full transactional documents, reviews different document versions, and responds to legal questions while staying grounded in the legal context.
Key Features
- Legal research assistance: Quickly finds relevant case law, statutes, and regulations while accounting for legal context and jurisdictional nuance.
- Contract review: Analyzes contracts, flags potential risks, and surfaces issues across full transactional documents.
- Deposition preparation: Helps attorneys organize key points, review testimony, and prepare outlines with less manual effort.
- Legal document summarization: Extracts critical details from lengthy documents and multiple document versions.
- Case analysis: Identifies key arguments, supporting evidence, and relevant precedents to support actionable intelligence.
Pros
- Finds case law and statutes faster than manual searches
- Flags risks and missing clauses with AI-powered insights
- Automates repetitive tasks, reducing workload for legal teams
- Designed for easy adoption without a steep learning curve
3. ChatGPT
ChatGPT isn’t designed specifically for law firms (or legal practice, for that matter), but many in the legal industry use it as a general-purpose AI for a wide range of legal-adjacent tasks.
From drafting emails and summarizing case law to generating legal arguments and reviewing long documents, it serves as a flexible AI-powered legal assistant.
Source: ChatGPT.com
While it doesn’t replace specialized legal AI tools, lawyers often rely on ChatGPT to answer questions, produce first drafts, brainstorm ideas, and refine legal writing before final review.
Key Features
- Legal writing assistance: Helps draft contracts, emails, and legal memos with clear, structured language suitable for first drafts.
- Document summarization: Condenses case law, statutes, and long legal documents into digestible summaries.
- Legal research support: Helps locate case law, statutes, and legal concepts, though outputs require verification.
- General productivity support: Assists with scheduling, transcription, simple legal services, and other administrative tasks.
Pros
- Useful for research, writing, and general legal-adjacent tasks
- Quickly generates drafts, summaries, and contract reviews
- More accessible than many specialized legal AI apps or tools
- No complex setup or integrations required
4. ContractSafe
ContractSafe is a contract repository tool that helps teams store, search, and keep track of agreements in one place.
Managing contracts often gets messy fast. Deadlines creep up, key terms hide in long documents, and files end up scattered across shared drives, inboxes, and old folders. When that happens, even a simple check can turn into a slow hunt through paperwork.
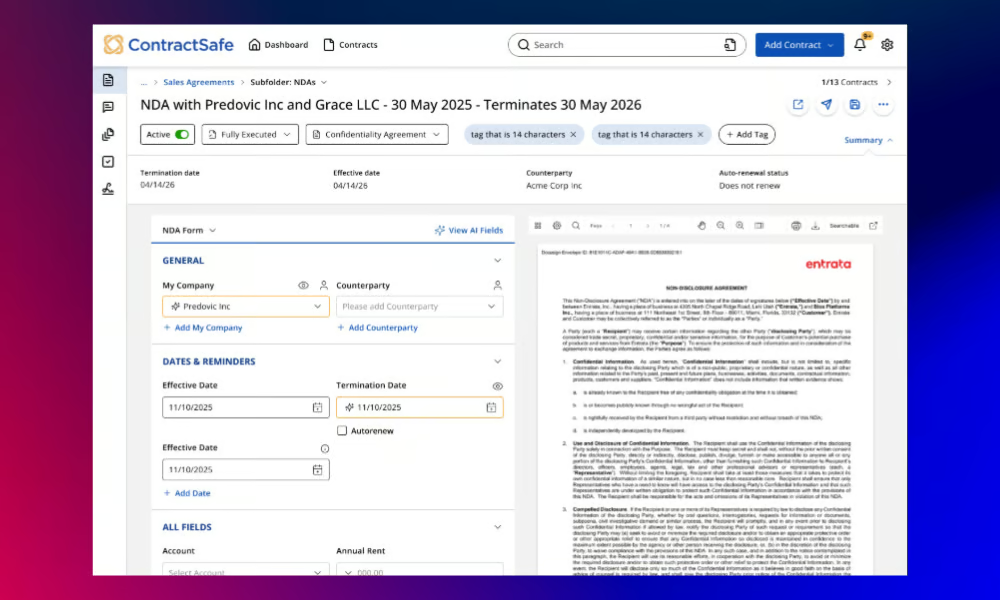
Source: G2
ContractSafe cuts through that clutter by giving contracts a single home. You can search across documents the same way you would search legal briefs, pulling up specific clauses, names, or dates in seconds.
Behind the scenes, it organizes legal data across a vast database of agreements. At the same time, automated reminders help teams stay on top of renewals and obligations, and secure storage keeps sensitive files protected.
It stays focused on organization and tracking rather than drafting or reviewing full contracts. For teams that need clarity around active agreements, deadlines, and responsibilities, ContractSafe offers a straightforward way to keep contract work moving without adding friction.
Key Features
- AI-powered search: Instantly locates contract terms, clauses, and key details within complex documents using simple keyword searches.
- Automated deadline reminders: Send alerts before renewals, expirations, or other important obligations tied to active agreements.
- Secure document storage: Keeps contracts centralized and searchable for faster attorney review.
- User permissions & access control: Controls who can view, edit, or download contracts across teams.
- Integrations with business tools: Connects with CRMs and document management platforms to fit into existing systems.
Pros
- Makes finding contracts quick and easy
- Prevents missed deadlines with automated reminders
- No complex setup or IT support needed
- Supports team collaboration with access controls
5. DocuSign
DocuSign makes signing and managing legal documents faster, more secure, and fully digital.
With legally binding e-signatures and automated workflows, it helps businesses and law firms move agreements forward without the friction of printing, scanning, or mailing documents back and forth.
Source: G2
While DocuSign is best known for e-signatures, its platform has expanded to support broader legal document workflows used by transactional lawyers and corporate legal departments.
Tools like DocuSign Iris add AI capabilities that assist with due diligence, document review, and data extraction. These features help teams work through agreements more efficiently while staying aligned with client service expectations.
These features support agentic workflows and custom legal workflows that fit into existing processes, making DocuSign a fully integrated option for managing agreements from signature through storage and tracking.
Key Features
- Legally binding e-signatures: Allows users to sign documents securely from anywhere, across devices.
- Automated contract workflows: Supports custom workflows for sending, signing, approving, and finalizing agreements.
- AI-assisted review with Iris: Helps surface key terms and insights during due diligence and contract review.
- Audit trails & compliance tracking: Maintains a detailed activity record to support compliance and internal review.
- Secure cloud storage and integrations: Connects with legal CRM, document management, and legal systems to stay fully integrated.
Pros
- Speeds up contract signing with secure e-signatures
- Supports due diligence and review with AI-assisted tools
- Fits into custom, agentic workflows across teams
- Accessible across devices for remote and distributed work
6. MyCase
MyCase simplifies document storage with a secure, cloud-based document management system built specifically for law firms.
Source: G2
MyCase helps attorneys store, access, and manage case data in one centralized location to reduce the risk of lost files and version confusion. Documents stay connected to the right matters, clients, and deadlines, which supports consistency and data security across the firm.
While MyCase offers broader practice management tools, its document storage features focus on keeping sensitive client information protected, searchable, and easy to work with, whether files originate in Microsoft Word or are uploaded from other sources.
Overall, the platform is designed to support everyday workflows while helping firms ensure compliance with internal policies and security expectations.
Key Features
- Cloud-based document storage: Keeps legal files organized and accessible from any device.
- Advanced search & tagging: Uses filters and keyword searches to quickly locate legal content tied to specific cases.
- Role-based access control: Manages who can view, edit, or download documents containing sensitive client information.
- Client portal integration: Allows secure document sharing without email attachments.
- Automatic backups & security encryption: Protects case data and supports data security and compliance needs.
Pros
- Keeps all legal documents in one secure location
- Makes it easy to search and retrieve case files
- Allows controlled access for clients and team members
- Provides cloud-based access for remote work
7. Harvey AI
AI models are making legal work faster and more efficient, and Harvey AI is one of the newest tools built specifically for law firms.
Source: Harvey.ai
Designed to assist with legal research, contract review, and document analysis, Harvey AI helps lawyers process large amounts of information quickly while maintaining accuracy.
No type of artificial intelligence can be a total replacement for human legal expertise, of course. Nevertheless, many firms use Harvey AI to speed up repetitive tasks, analyze legal documents, and improve decision-making.
Key Features
- AI-powered legal research: Finds relevant case law, statutes, and legal precedents in seconds.
- Contract analysis & review: Identifies key clauses, missing terms, and potential risks in agreements.
- Litigation support: Assists with drafting briefs and legal arguments and summarizing case details.
- Document summarization: Extracts important points from long legal documents to save time.
- Natural language processing: Understands complex legal language and provides insights based on queries.
Pros
- Speeds up legal research by quickly retrieving relevant cases
- Helps identify risks and missing clauses in contracts
- Reduces the time spent summarizing lengthy legal documents
- Uses advanced AI to interpret legal language accurately
Start Automating Your Biggest Bottleneck With Briefpoint
Discovery work tends to be the slowest, most repetitive part of litigation. Drafting requests, organizing responses, tracking productions, and double-checking formatting can quietly consume days that could be spent on higher-value legal work.

Briefpoint targets that bottleneck directly. It handles the repetitive structure and formatting of discovery while keeping attorneys firmly in control of review and strategy. Everything stays in Word, so the process feels familiar and easy to verify.
Autodoc extends that workflow into document production. It connects requests for production to the actual case files, identifies responsive documents, and generates written responses with page-level Bates numbering.
That means less time matching documents to requests and fewer manual steps before serving a production.
FAQs About AI for Legal Documents
What is the best AI for legal docs?
There’s no single “best” option for everyone. The right tool depends on what kind of work you handle. Some platforms focus on deep research across case law, while others support drafting or document organization. The most effective tools fit naturally into your workflow while keeping human oversight front and center.
Is Claude or ChatGPT better for lawyers?
Both can act as a helpful AI assistant for brainstorming, summarizing, and early drafts. ChatGPT tends to be more flexible across tasks, while Claude often handles longer documents well. Neither replaces practical law resources or professional judgment, so verification always matters.
Can AI help with legal documents?
Yes. AI can support everything from drafting legal document templates and reviewing contract language to organizing witness statements and preparing materials for the negotiation process. Used thoughtfully, these tools focus on enabling attorneys to work faster without cutting corners.
Can ChatGPT write legal documents?
ChatGPT can generate drafts, outlines, and plain-language explanations, which can be useful for law students, early-stage drafting, or business development work. Final documents should always be reviewed by a qualified professional to confirm accuracy, alignment with legal principles, and suitability for the legal profession.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only. Information on this website may not constitute the most up-to-date legal or other information.
This website contains links to other third-party websites. Such links are only for the convenience of the reader, user or browser. Readers of this website should contact their attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal matter. No reader, user, or browser of this site should act or refrain from acting on the basis of information on this site without first seeking legal advice from counsel in the relevant jurisdiction. Only your individual attorney can provide assurances that the information contained herein – and your interpretation of it – is applicable or appropriate to your particular situation. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website authors, contributors, contributing law firms, or committee members and their respective employers.